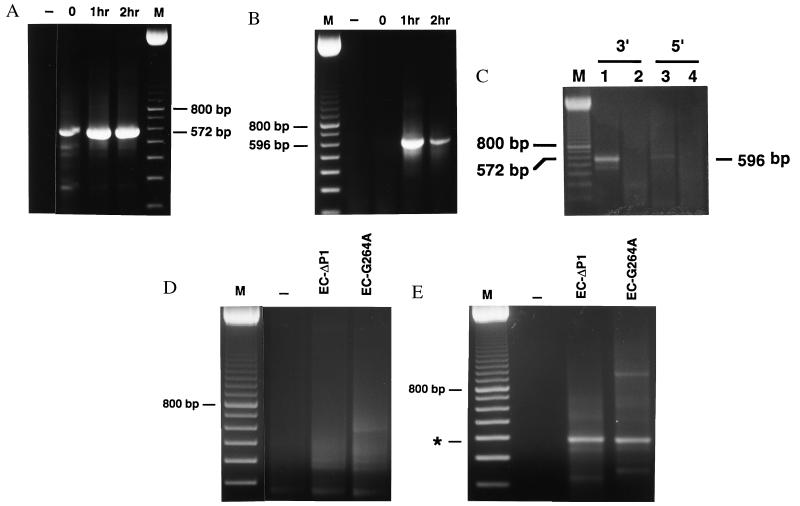
Figure 3.
RT-PCR amplification of intron–23S rRNA junctions. RNA was from cells transformed with pMALEC-IVS. Lanes: (–), no template; 0, 1, and 2 hr, time after IPTG induction; M, 100-bp ladder. (A) Amplification of 3′ integration junctions in 23S domain IV. Upstream primer (UPI-94) is intron-specific; downstream primer (DP-2180) anneals to 23S rRNA. The 572-bp product represents 3′ integration junctions at positions 1924, 1925, and 1926. (B) Amplification of 5′ integration junctions in 23S domain IV, with a 23S-specific upstream primer (UP-1666) and intron-specific downstream primer (DPI-336). The 596-bp fragment represents the 5′ integration junction at position 1926. (C) Lanes 1 and 3, total RNA from cells transformed with pMALEC-IVS after 2 hr of induction; lanes 2 and 4, in vitro transcribed intron RNA added during isolation of total RNA from cells transformed with pMAL-c2. RT-PCR as in A and B. (D) RT-PCR of splicing-defective mutants. Reactions as in A. RNA was from cells transformed with pLKEC-ΔP1 and pLKEC-G264A. (E) As in C, except using primers from B. ∗, 340-bp product of spurious single-primer amplification of intron RNA.