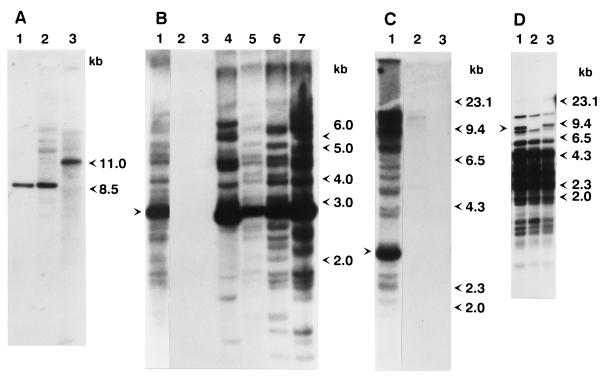
Figure 1.
Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from wild-type and mutant strains. (A) Ten micrograms of total DNA from strain 9 (lane 1), strain 160 (lane 2), and the yd mutant strain (lane 3) was digested with HindIII and subjected to Southern blot analysis using the SalI–EcoRI fragment of a D. melanogaster yellow-containing clone (16) as a probe. (B) Genomic DNA from various D. virilis strains and mutants isolated from the progeny of dysgenic crosses was digested with XhoI and probed with the XhoI fragment of Penelope. Lanes: 1, strain 160; 2, strain 2; 3, strain 9; 4, white mutant; 5, sn25 mutation; 6, revertant of sn25 mutation; 7, yd mutation. The arrow indicates the position of the 2.8-kb band. (C) Genomic DNA of various D. virilis strains was digested with BamHI and subjected to Southern blot analysis. Lanes: 1, strain 160; 2, Pasadena strain; 3, Krasnodar strain. The arrow indicates the position of a prominent 2.7-kb band present in all strains containing Penelope. (D) DNA from strain 9 (lane 2) and two independent droop mutants (lanes 1 and 3) obtained from the progeny of embryos injected with Penelope-containing clones were digested with EcoRI and HindIII and hybridized with a probe containing an internal SalI–BamHI fragment of the Ulysses element. The arrow indicates an additional restriction fragment seen in both droop mutant strains.