Fig. 5.
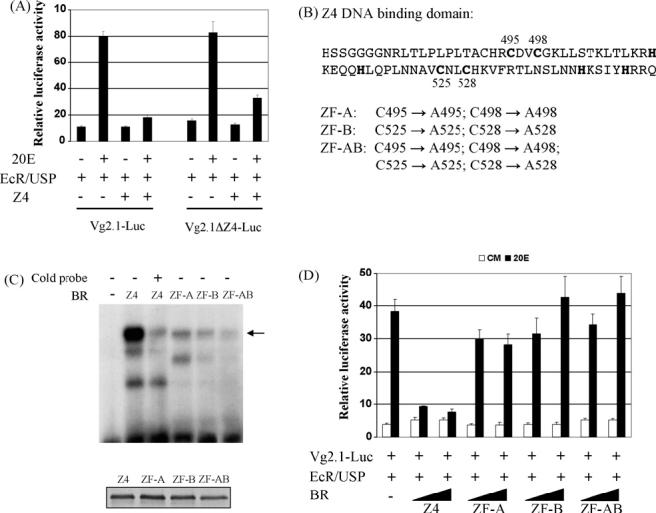
Regulation of the Vg promoter requires intact DNA binding domains of BR. (A) Drosophila L57 cells were co-transfected with expression vectors for AaEcR-B, AaUSP-B, AaBR-Z4, and indicated reporter plasmids. In pVg2.1ΔZ4-Luc, all seven identified potential Z4 binding sites were removed by point mutagenesis. After transfection, cells were cultured in medium with or without 1 × 10-6 M of 20E. Data represent the ratios of firefly luciferase to Renilla luciferase activity (relative luciferase activity). (B) Point mutations were introduced into the Z4 DNA binding domain. The cystidines targeted in the zinc fingers are highlighted in the amino acid sequence. (C) EMSA was performed using 32P-labeled oligonucleotide containing consensus Drosophila BR-Z4 binding site and in vitro-synthesized mosquito Z4 and its mutants. A 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled probe was added as specific competitor. When the Z4 proteins were synthesized, an in vitro coupled transcription and translation (TNT) reaction was performed in parallel in the presence of 35S-methionine. The autoradiograph of the TNT products is shown at the bottom, indicating that comparable amounts of individual Z4 proteins were added in the EMSA experiment. (D) Drosophila L57 cells were co-transfected with pVg2.1-Luc reporter, expression vectors for AaEcR-B and AaUSP-B, and indicated AaBR-Z4 constructs. The solid triangle represents increasing amounts of the Z4 expression plasmids.
