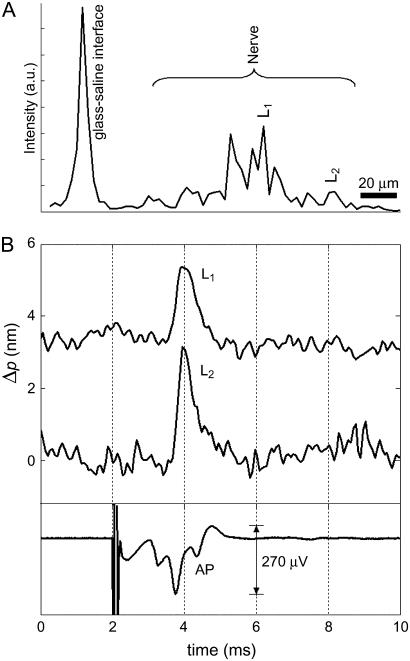
FIGURE 3.
Optical detection of AP propagation in a crayfish leg nerve. (A) Depth profile showing the glass-saline interface and multiple surfaces within the nerve. Labels L1 and L2 indicate two locations inside the crayfish nerve. (B) Optical path length changes due to transient displacement during AP propagation at locations L1 and L2 and corresponding compound AP recorded differentially with respect to ground by a pair of platinum electrodes that are placed before and after the optical read-out area. Transient increase in optical signal represents a displacement toward the reference glass surface. Stimulus (1 mA, 50 μs) is presented at 2 ms and caused a localized artifact in the electrical measurement. Fifty responses are averaged in each trace.