Figure 2.
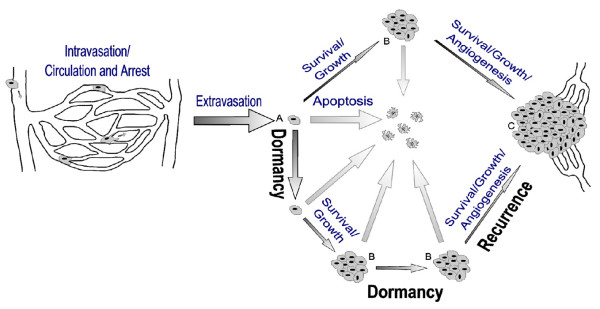
Upon arriving in a secondary site the majority of metastatic cells extravasate and proceed to one of three possible fates: they can undergo cell death (apoptosis), remain dormant or begin proliferating. In order to form a large, vascularized and clinically relevant metastatic tumour (C), a single cell must begin and continue proliferating as well as acquire a vasculature by angiogenesis. Dormant single cells (A) and micrometastases (B) are possible sources of recurrent cancer.
