Figure 3. PAP-1 inhibits the elicitation phase of ACD when administered i.p., orally, or topically.
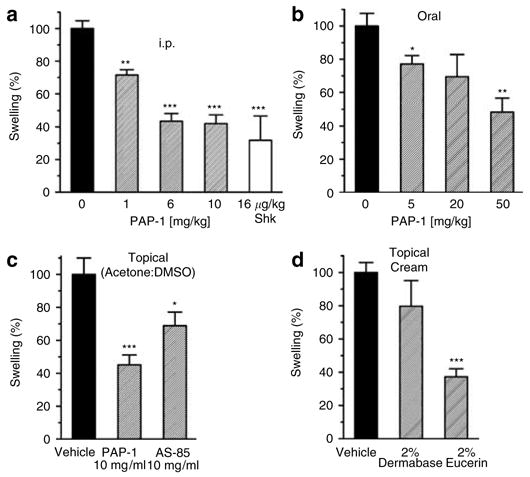
(a) Rats were treated i.p. with the vehicle Cremophor®EL/PBS (n = 30), PAP-1 at 1mg/kg (n = 9, 71.5±3.3% of control, P = 0.002), 6mg/kg (n = 20, 43.5±4.8% of control, P = 0.000001), 10 mg/kg (n = 16, 42.0±5.4% of control, P = 0.000001), or with ShK at 16 μg/kg (n = 3, 31.8±14.9% of control, P = 0.00015 vs control and P = 0.45 vs 10 mg/kg PAP-1). (b) Rats were gavaged with the vehicle peanut oil (n = 5) PAP-1 at 5mg/kg (n = 5, 77.2±5.0% of control, P = 0.037), 20 mg/kg (n = 5, 69.5±13.3% of control, P = 0.081) or 50mg/kg (n = 5, 48.4±8.2% of control, P = 0.002). (c) Rats were treated topically on the ears with 50 μl of the vehicle acetone:DMSO (n = 10), PAP-1 at 10 mg/ml (n = 10, 45.1±6.1% of control, P = 0.0002) or AS-85 at 10mg/ml (n = 9, 68.9±8.2% of control, P = 0.03). (d) PAP-1 was applied as a 2% cream in Dermabase™ (n = 7, 79.8±15.4% of control, P = 0.15) or Eucerin® (n = 8, 37.2±4.8% of control, P = 0.000001). The controls (n = 14) were treated either with “empty” Dermabase™ (n = 7) or Eucerin® (n = 7) and the results (181 μm swelling) averaged as there was no significant difference between the two vehicles. Values are given as the mean±SEM of swelling in percent. The average ear swelling in all controls from all conditions was 168.5 μm.
