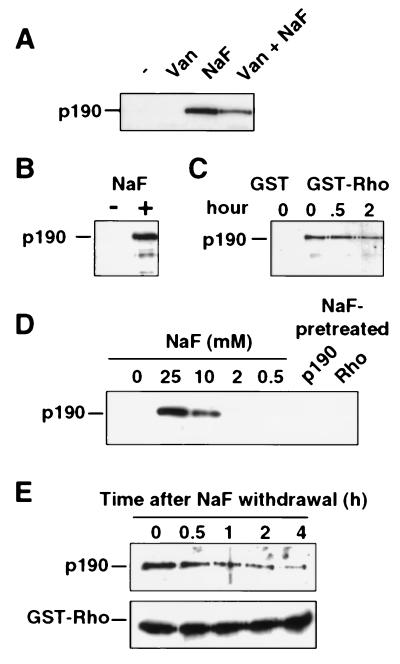
Figure 1.
Fluoride stabilizes a high-affinity complex between the RhoA GTPase and p190 RhoGAP. Recombinant GST-RhoA protein (GDP-loaded) immobilized on glutathione beads was used in a p190-binding assay with either fibroblast extract (A and C) or recombinant baculovirus-produced p190 (B, D, and E). After 1 h of incubation, beads were washed three times and complex formation with p190 was analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting using an anti-p190 antibody or an anti-GST-specific antibody. (A) The binding reaction was either unsupplemented (−) or supplemented with 1 mM sodium orthovanadate (Van), 20 mM NaF, or both (Van+NaF), as indicated. (B) Highly purified baculovirus-produced p190 was incubated with GST-RhoA in the presence or absence of 20 mM NaF. (C) Cell extracts lysed in the absence of NaF were incubated at 37°C for 0, 0.5, or 2 h before incubation with GST or GST-RhoA in the presence of NaF for 1 h at 4°C. (D) Similar p190–Rho binding assays were performed in the presence of a range of NaF concentrations (as indicated). In lanes p190 and Rho, p190 or RhoA were pretreated for 1 h with 20 mM NaF before a binding assay in which the final concentration of NaF was reduced to 2 mM NaF. (E Upper) The RhoA–p190 complex was formed in the presence of 20 mM NaF, and the washed beads were incubated in NaF-free buffer for the indicated times and then assayed for retention of p190. (E Lower) An anti-GST antibody reveals equivalent amounts of GST-RhoA.