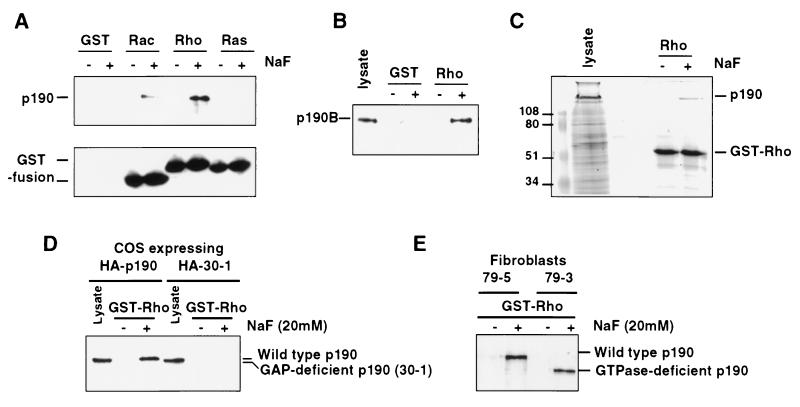
Figure 2.
High-affinity fluoride-promoted RhoA–p190 complex requires a functional p190 RhoGAP domain. (A) GTPase binding assays were performed with baculovirus p190 using recombinant GST, GST-Rac, -Rho, or -Ras proteins. p190 (Upper) and GST fusion proteins (Lower) were detected by immunoblotting. Unfused GST protein is not seen due to its low molecular weight. (B) Association of p190-B (from extracts of Swiss 3T3 cells) with RhoA is also fluoride-dependent as revealed by GST-RhoA binding assays. (C) Coomassie blue staining of an SDS/PAGE gel of crude baculovirus-infected cell lysate overexpressing p190 and GST-RhoA association with p190 specifically in the presence of NaF. (D) Cos-7 cells were transfected with vectors expressing a hemagglutinin-tagged form of either wild-type p190 (HA-p190) or p190 deleted of the RhoGAP domain (HA-30–1), and lysates were subjected to a RhoA binding assay in the presence or absence of NaF. Expression (lysates) and GST-RhoA-associated p190 were detected with anti-hemagglutinin antibodies. (E) Lysates from fibroblasts expressing either wild-type p190 (79–5) or a GTPase-deleted form of p190 (79–3) were subjected to a similar RhoA binding assay.