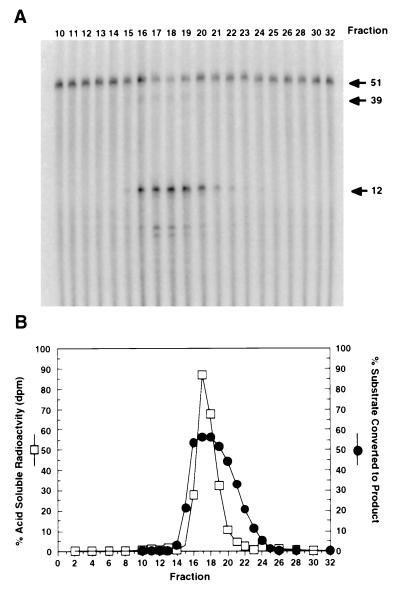
Figure 1.
RNase HI contains both a structure-specific and random endonucleolytic activity. Aliquots (1 μl) of each fraction from the final column of the first preparation (Mono-Q) were diluted 1:4000 and tested for both RNase HI structure-specific and random cleavage activity. (A) To generate a model Okazaki substrate, an internally radiolabeled (32P)RNA13nt was extended with DNA38nt and annealed to a DNA template. Aliquots of the diluted fractions were assayed at 37°C for 10 min. Cleavage results in a specific RNA12nt fragment and an oligonucleotide39nt containing the remaining ribonucleotide and deoxynucleotides (indicated by arrows). (B) Random RNase HI cleavage was assayed on a [3H]poly(rA)/oligo(dT) substrate. RNase HI activity degrades the substrate releasing small oligonucleotides into the acid soluble fraction that were quantitated by scintillation counting. The percent of acid soluble radioactivity (□) was determined for each fraction. Additionally, the percent of the Okazaki fragment substrate converted to the RNA12nt product in A was determined and also plotted (•).