Figure 5. Model for role of ID proteins in regulating neuronal maturational differentiation.
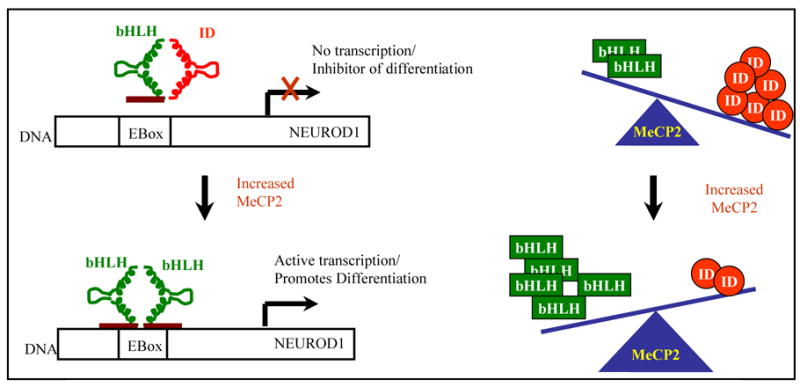
In immature neurons with high expression of ID proteins, heterodimers of bHLH-ID prevent DNA binding and expression of differentiation associated genes like NEUROD1. Upon neuronal maturation, elevated levels of MeCP2 repress the expression of ID genes, resulting in functional bHLH-bHLH dimers that can bind to E-box DNA sequences and activate transcription of differentiation associated genes such as NEUROD1, ASCL1 and NEUROG1.
