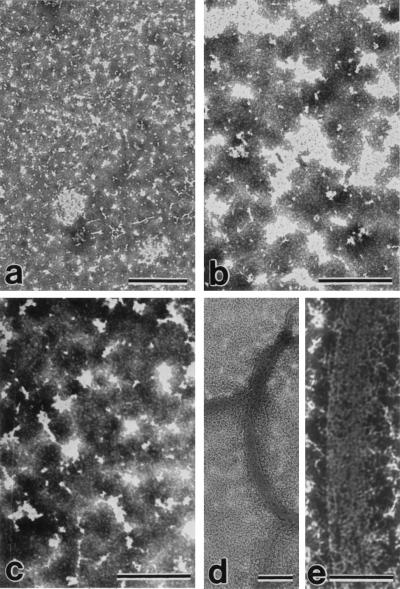
Figure 2.
Electron micrographs showing the products of association of AD P-tau with tau, MAP1, and MAP2 negatively stained with phosphotungstic acid. MAP1– and MAP2–AD P-tau aggregates were induced as described in Fig. 1. Under identical conditions, 150 μg of normal tau and 8 μg of AD P-tau/100 μl also were incubated. Aliquots of the incubated mixture of MAP1 and AD P-tau (a), MAP1 alone (b), MAP2 and AD P-tau (c), or tau and AD P-tau (d and e) were taken after centrifugation and were examined by negative stain electron microscopy. Association of AD P-tau with only tau and not MAP1 or MAP2 resulted in the formation of filaments/tangles. (Bars = 1 μm for a and d; 0.5 μm for b, c, and e.)