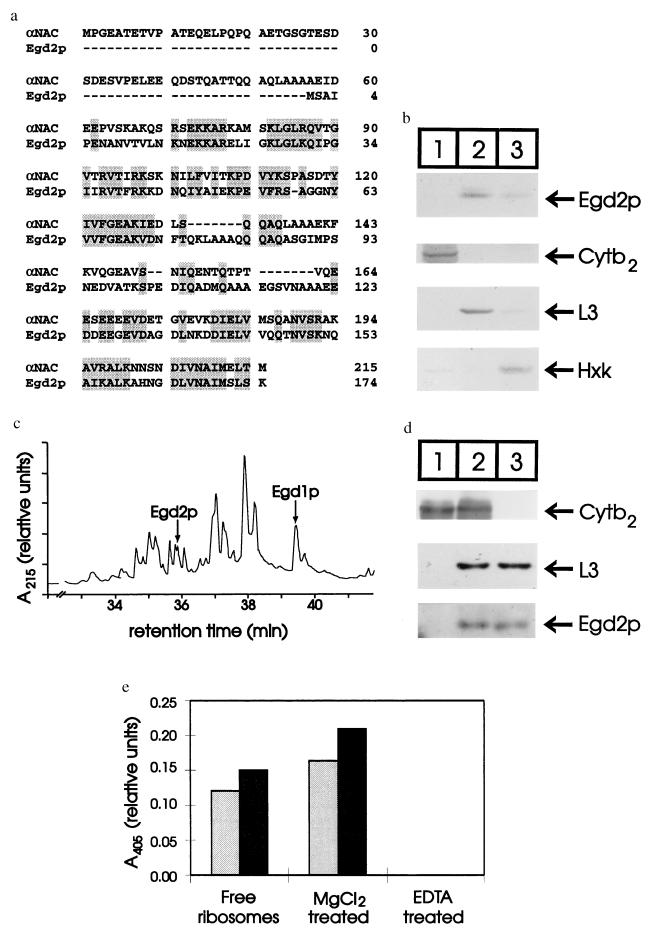
Figure 1.
The yeast αNAC homolog Egd2p is associated with free ribosomes. (a) Amino acid sequence alignment of bovine αNAC (11) with the Saccharomyces cerevisiae homolog Egd2p (39). Residues conserved between the two sequences are shaded. (b) Wild-type yeast cells were separated into mitochondria (lane 1), ribosomes (lane 2), and cytosol (lane 3) and were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting against Egd2p, cytochrome b2 (cyt b2), ribosomal protein L3, and the cytosolic enzyme hexokinase (Hxk). (c) Yeast ribosomes were extracted with high salt, and the extracted proteins were separated by reversed phase HPLC. (d) Mitochondria purified in buffers containing 10 mM EDTA (100 μg of total protein; lane 1) or mitochondria purified in buffer containing 2 mM MgCl2 (100 μg of total protein; lane 2) and free ribosomes (≈2 μg of total protein; lane 3) were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting. (e) The presence of Egd2p (black bars) relative to ribosomal protein L3 (gray bars) was analyzed in samples of free ribosomes (≈2 μg total of protein), mitochondria purified in buffers containing 2 mM MgCl2 (100 μg total of protein), or mitochondria purified in buffer containing 10 mM EDTA (100 μg total of protein). Proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and blotted to nitrocellulose, and then strips corresponding to the position of Egd2p or L3 were excised, processed, and incubated with p-nitrophenolphosphate.