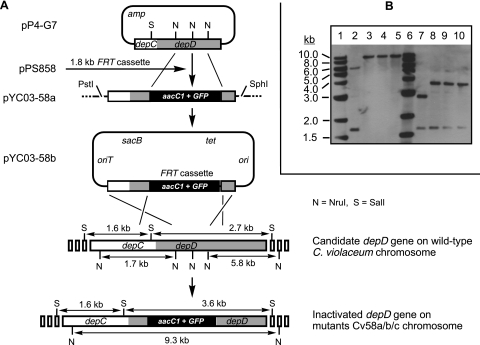
FIG. 3.
Creation of depD-inactivated mutant strains by targeted gene replacement. (A) Construction of gene replacement vector pYC03-58b and homologous recombination via double crossover between the vector and the bacterial chromosome to generate a mutant genotype. (B) Southern analysis of the genotypes of wild-type and depD-inactivated mutant strains of C. violaceum, using the labeled 2.6-kb insert DNA of pP4-G7 as a probe. Genomic DNA was digested with NruI (lanes 2 to 5) or SalI (lanes 7 to 10). Lanes 1 and 6, 1-kb DNA ladders (New England Biolabs), hybridized with their digoxigenin-labeled probes; lanes 2 and 7, DNA from the wild-type strain; lanes 3 to 5 and 8 to 10, DNA from independent mutant strains Cv58a, Cv58b, and Cv58c, respectively. A change in the pattern of positively hybridized DNA bands indicates targeted gene inactivation.