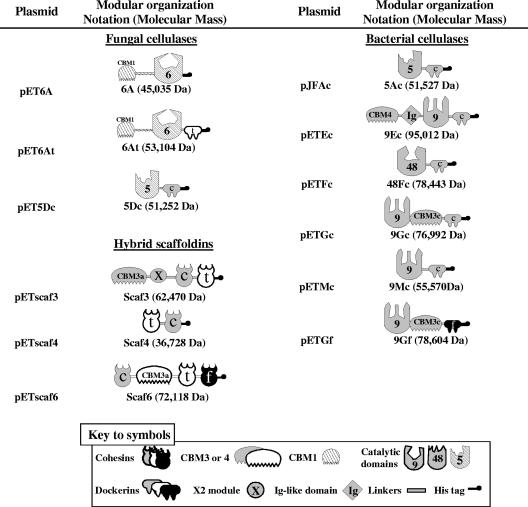
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the recombinant proteins used. Gray (C. cellulolyticum), white (C. thermocellum), black (R. flavefaciens), and hatched (N. patriciarum) denote the sources of the respective modules (see key to symbols). In the shorthand notation for the engineered enzymes, numbers refer to the corresponding GH family of the catalytic module; A, D, E, F, G, and M refer to the original names of the enzymes (CelA and CelD from N. patriciarum and CelA, CelE, CelF, CelG, and CelM from C. cellulolyticum); c, f, and t indicate the sources of the dockerin modules of C. cellulolyticum, R. flavefaciens, and C. thermocellum, respectively. Note that, unlike CBM1 of the fungal enzyme and CBM3a of the scaffoldins, the CBMs (CBM3c and CBM4) associated with the C. cellulolyticum enzymes 9Gf, 9Gc, and 9Ec are not CBMs per se but serve as ancillary modules that modify the activity of the catalytic modules of the parent enzyme. The X2 module in Scaf3 is a 100-residue-long module that the scaffoldin CipC contains and whose functions remain unknown. Ig, immunoglobulin.