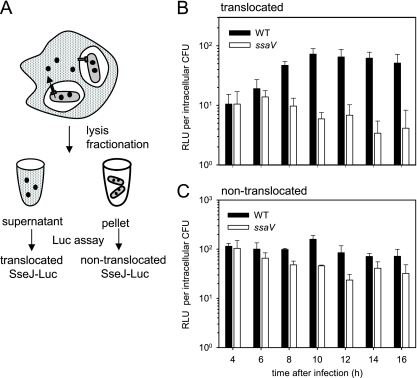
FIG. 5.
Translocation of an SseJ-Luc fusion protein by intracellular S. enterica. (A) Outline of the experimental procedure. RAW264.7 cells were infected with the S. enterica serovar Typhimurium WT or the ssaV strain, deficient in the SPI2-encoded T3SS. Both strains harbored a translation fusion of luc to codon 200 of sseJ, encoding a translocated effector protein of the SPI2-T3SS. At various time points after infection, host cells were lysed and the number of intracellular bacteria was determined. After centrifugation of the lysates, the Luc activities in the supernatant fractions were determined for quantification of translocated SseJ-Luc (B). In addition, the pellet fraction was subjected to lysis of bacterial cells, and Luc assays were performed to quantify cell-associated, nontranslocated SseJ-Luc (C). Luc activities are expressed as RLU per intracellular CFU in order to compensate for intracellular replication over time and different replication rates of WT and ssaV strains. Means and standard deviations for infections with the WT and the ssaV strain are shown for one representative experiment of three.