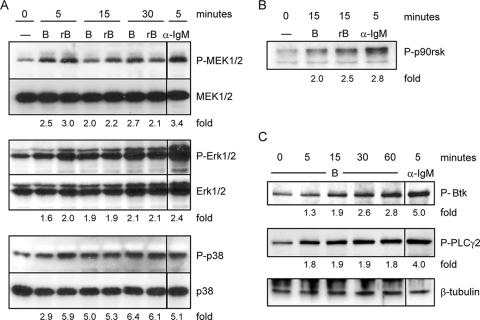
FIG. 2.
CT-B induces specific phosphorylation events in B cells. Primary splenic B cells from C3H/HeJ mice were either left untreated (0 min) or stimulated with 10 μg/ml CT-B or rB for the times indicated and were harvested together at the end of the experiment. Cells were stimulated with 10 μg/ml anti-IgM F(ab′)2 as a positive control. Whole-cell lysates were generated, and this was followed by separation of cellular proteins by SDS-PAGE and transfer to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane for immunoblotting. Phospho-MAP kinases (A), phospho-p90rsk (B), and phospho-Btk and phospho-PLCγ2 (C) were detected. Equal sample loading was confirmed by reprobing for total MAP kinase (A), a lower-molecular-weight nonspecific band (B), or β-tubulin (C). The mean intensity of each phosphoprotein band was normalized to the corresponding control, and the fold increases for phosphoproteins from treated samples compared to proteins from untreated samples are indicated.