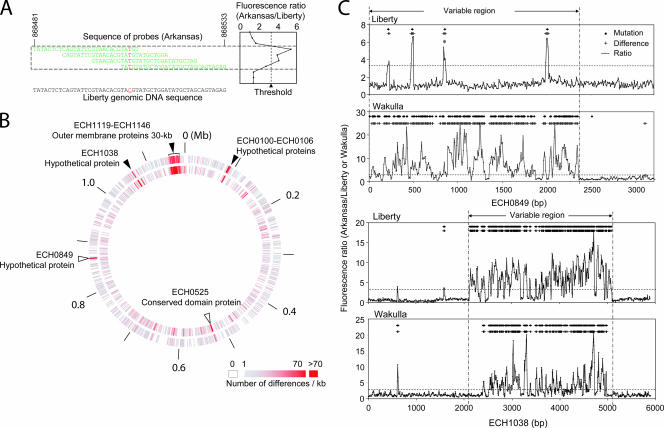
FIG. 1.
CGH of E. chaffeensis strains. (A) Multiple overlapping probes cover each nucleotide. A mutation at a site, indicated by red, perturbs hybridization of the sample to all probes. The representative example is a mutation in Liberty ECH_0849, indicated by an asterisk in panel C. The sequence of probes on one of the strands is represented. (B) E. chaffeensis strains Wakulla and Liberty were compared with the Arkansas strain using an array containing a total of 294,050 29-mer probes spaced, on average, every 8 bp throughout the genome of E. chaffeensis Arkansas. Inner circle, Arkansas versus Liberty; outer circle, Arkansas versus Wakulla. The open and solid arrowheads indicate remarkably different regions. (C) ECH_0849 and ECH_1038: CGH results revealed different positions and actual mutations. Sequencing was used to validate the sensitivity and specificity of CGH. The horizontal dotted line indicates the threshold of the Cy3/Cy5 ratio used to indicate a difference. The diamonds and plus signs indicate positions of mutated bases and probes with differences, respectively. The variable regions of ECH_0849 and ECH_1038 in the Wakulla and Liberty strains compared with strain Arkansas are between two vertical dashed and dotted lines.