FIG. 1.
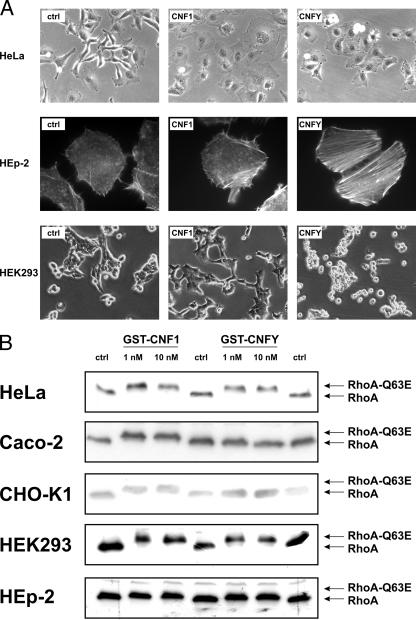
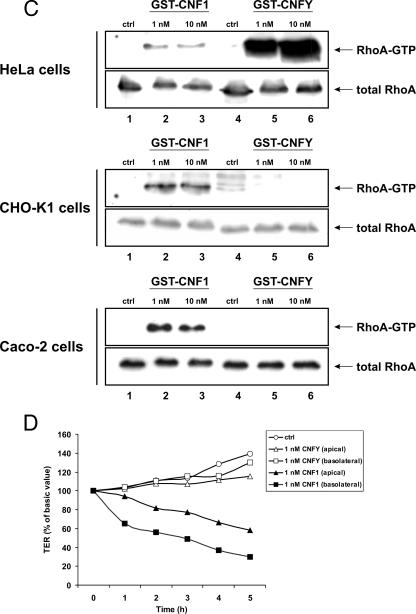
Cellular responsiveness to CNF1 and CNFY. (A) HeLa cells, HEK293 cells, and HEp-2 cells were treated with 1 nM GST-CNF1 or 1 nM GST-CNFY at 37°C overnight. Toxin-induced morphological changes were studied by phase-contrast microscopy or fluorescence microscopy of actin-stained cells. (B) HeLa cells, CHO-K1 cells, Caco-2 cells, HEK293 cells, and HEp-2 were treated with GST-CNF1 and GST-CNFY at 37°C for 3 h at the concentrations indicated. Cells were lysed, and a Rho shift assay was performed. (C) HeLa cells, CHO-K1 cells, and Caco-2 cells were incubated with GST-CNF1 or GST-CNFY for 4 h at 37°C using the concentrations indicated. After lysis of the cells, 1/10 of each sample was subjected to Western blot analysis. The main sample volume (9/10 of the sample) was incubated with the GTPase-binding domain of GST-rhotekin coupled to beads to examine the RhoA activation status by a pull-down assay. For detection of total RhoA and activated RhoA an anti-RhoA antibody was used for Western blotting. (D) Effect of GST-CNF1 and GST-CNFY on the TER of Caco-2 cells. GST-CNF1 (1 nM) and GST-CNFY (1 nM) were applied apically as well as basolaterally to cellular monolayers growing on filter inserts; untreated cells (ctrl) were also included. Cells were incubated at 37°C, and the TER was measured at the times indicated. The graph presents data from one typical experiment representative of three independent experiments performed.