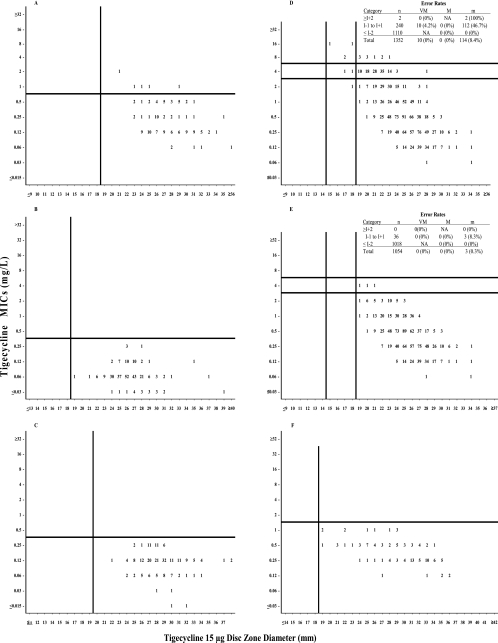
FIG. 1.
Scattergrams of tigecycline MICs versus zone diameters (15-μg disks). (A) All staphylococci combined (including methicillin-resistant isolates; n = 130), (B) Streptococcus pneumoniae (n = 209) and nonpneumococcal streptococci (n = 60) combined, (C) all Enterococcus spp. combined (n = 216), (D) all Enterobacteriaceae combined (n = 1,352) (122/125 [97.6%] of the isolates with a tigecycline MIC of ≥4 μg/ml were Morganella, Proteus spp. other than P. vulgaris, or Providencia spp.), (E) Enterobacteriaceae without Morganella, Proteus spp. other than P. vulgaris, or Providencia spp. (n = 1,054), (F) Haemophilus spp. (n = 113). Horizontal lines represent proposed susceptible (lower line) and resistant (upper line) MIC breakpoints; vertical lines represent proposed susceptible (right line) and resistant (left line) zone diameter breakpoints. Abbreviations: n, number of strains tested; VM, very major errors; M, major errors; m, minor errors; I+2, intermediate MIC breakpoint plus 2 log2 dilutions; I−1 to I+1, intermediate MIC breakpoint plus or minus 1 log2 dilution; I−2, intermediate MIC breakpoint minus 2 log2 dilutions.