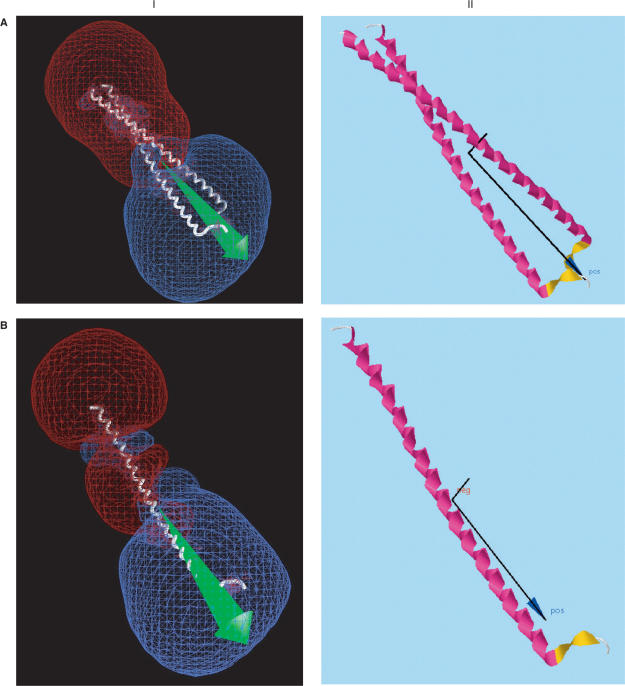
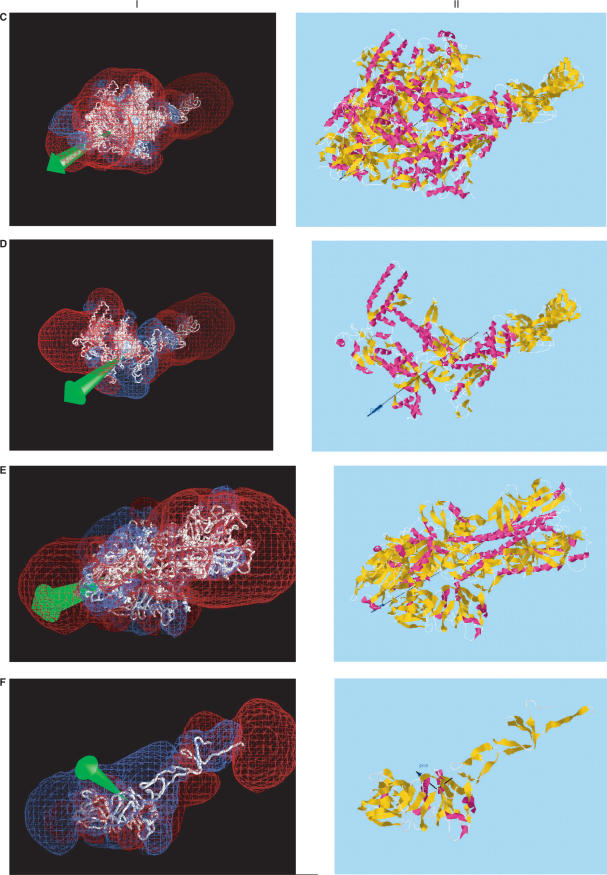
Figure 2.
Comparison of dipole moments calculated using (I) GRASP (2), displaying the dipole vector in green and –12 kT/e (red) and +12 kT/e (blue) isopotential surfaces; (II) Protein Dipole Moment Server (PDMS), showing the dipole moment vector in black, with a dark blue arrowhead, and the mass moment vector without an arrowhead. The same molecular orientations and modified Parse 3 partial atom charges were used, without hydrogens. (A) 1gd2: BZIP transcription factor PAP1 bound to DNA; 2 chains, 1051 atoms, 129 residues, mean radius 300 Å, charge +10, dipole moments 3328 D (I, GRASP) and 3032 (II, PDMS), with an angle of 2° between their vectors. This pattern is typical of several DNA-binding proteins, including 2dgc, yeast GCN4 Leu zipper, and 1dh3, mouse CREB BZIP-CRE complex, all of which are highly elongated and project a large region of negative potential into the region binding the positively charged DNA. (B) 1gd2, Chain E: 530 atoms, 65 residues, mean radius 212 Å, charge +4, dipoles 1747 D (I, GRASP) and 1591 D (II, PDMS) D, making an angle of 1°. (C) 1ynj: TAQ RNA polymerase. 6 chains, 24 309 atoms, 2821 residues, mean radius 2821 Å, charge –52, dipoles 6532 D (I, GRASP) and 6541 D (II, PDMS), making an angle of 3°. The putative DNA binding region is near the lower left. (D) 1ynj Chain D. 9602 atoms, 1238 residues, mean radius 1924 Å, charge –13, dipoles 8311 D (I, GRASP) and 9414 D (II, PDMS), making an angle of 6°. (E) 1flc: Hemagglutinin-esterase fusion glycoprotein of influenza virus. 6 chains, 13 700 atoms, 1767 residues, mean radius 1718 Å, charge –21, dipoles 7725 D (I, GRASP) and 7971 D (II, PDMS), making an angle of 1°. The acetylsialic acid binding domain is at the lower left. (F) 1flc Chain A. 3339 atoms, 427 residues, mean radius 598 Å, charge +5, dipoles 411 D (I, GRASP) and 411 D (II, PDMS), making an angle of 1°.