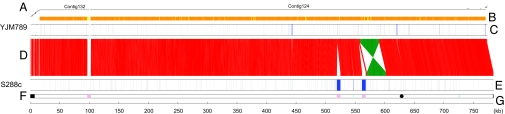
Fig. 1.
Alignment of the chromosome XIV sequences from YJM789 and S288c. (A) YJM789 contigs mapped to their locations on the S288c genome. (B) Sequence similarity between YJM789 contigs with a length of at least 10 kb and their corresponding sequences of S288c represented by color and coded from yellow (low) to orange (high). (C) Sequences of ≥100 bp that are present in YJM789 but absent in S288c are represented by blue lines. Similar sequences of <100 bp are represented by gray lines. (D) Sequence alignment between YJM789 and S288c chromosome XIV. Identical sequences are linked by lines. Red represents forward alignment. Green represents reverse complementary alignment. (E) Sequences of ≥100 bp that are absent in YJM789 but present in S288c are represented by blue lines. Similar sequences of <100 bp are represented by gray lines. (F) Repeat sequences of S288c are represented as follows: cyan rectangles, long terminal repeats; pink rectangles, retrotransposons; black rectangles, telomeres; black circle, centromere. (G) Coordinates of S288c in kilobase pairs.