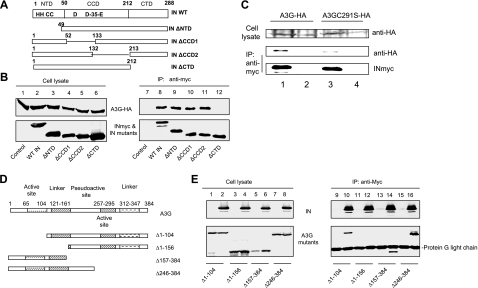
FIG. 5.
(A) The C terminus of HIV-1 IN and the first linker of A3G are required for the interaction of A3G and IN. HIV-1 IN domains and HIV-1 IN mutants used in this study are shown. (B) HA-tagged A3G expression vector was cotransfected with the INmyc expression vector or a control vector into 293T cells. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-HA MAb for the detection of A3G-HA and the anti-myc MAb for the detection of INmyc (lanes 1 to 6). Cell lysates were also immunoprecipitated (IP) by the anti-myc MAb conjugated to protein G-agarose beads. Coprecipitated samples were analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-HA MAb for the detection of A3G-HA or the anti-myc MAb for the detection of INmyc (lanes 7 to 12). (C) HA-tagged A3G or A3GC291S expression vector was cotransfected with the INmyc expression vector or a control vector into 293T cells. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-HA MAb for the detection of A3G-HA and A3GC291S-HA. Cell lysates were also immunoprecipitated by the anti-myc MAb conjugated to protein G-agarose beads. Coprecipitated samples were analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-HA MAb for the detection of A3G-HA and A3GC291S-HA or anti-myc MAb for the detection of INmyc. (D) The A3G domains and A3G mutants used in this study. (E) A3G or mutant A3G was cotransfected with the myc-tagged IN expression vector or a control vector into 293T cells. At 48 h posttransfection, cells were lysed and analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-HA and anti-myc MAbs (lanes 1 to 8). Cell lysates were also immunoprecipitated by the anti-myc MAb conjugated to protein G-agarose beads. Coprecipitated samples were analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-HA MAb or anti-myc MAbs (lanes 9 to 16).