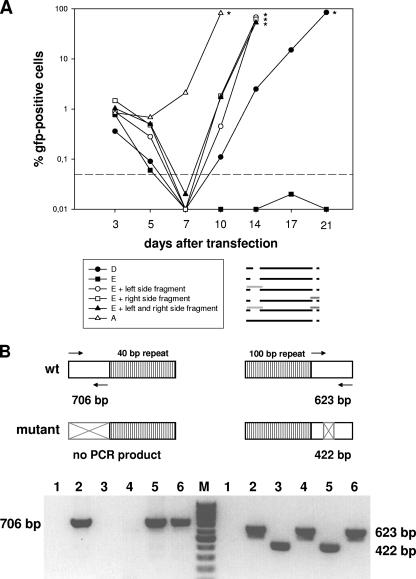
FIG. 4.
Kinetics of GFP expression after cotransfection of permissive BHK-21 cells. (A) Cells were transfected with 2 μg of BAC DNA of the double deletion mutant E, the double deletion mutant D, or the single deletion mutant A and, in cases of cotransfections, were additionally transfected with 4 μg of plasmid DNA carrying an unmutated genomic fragment spanning the mutated region. Cotransfection with either one or both such plasmids led to the reconstitution of infectious virus, as determined by an increase in the number of GFP-positive cells over timer after transfection. At the indicated times, cells were harvested and passaged. A part of the harvested cells was used to determine the number of GFP-positive cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis. The asterisks indicate the times when the particular cell cultures were stopped due to massive viral cytopathic effects. The dashed line indicates the detection limit, which was defined on the basis of the background fluorescence of untransfected BHK-21 cells. The pictogram schematically illustrates the mutants investigated, with the unmutated genomic fragments used for cotransfections represented as light and dark gray bars. Data shown are from a representative experiment which was repeated once with similar results. (B) (Top) PCR strategy to determine the presence or absence of either the wt or mutated genomic fragment in the genomes of the reconstituted viruses after cotransfection of BAC DNA of the double deletion mutant E with overlapping unmutated fragments spanning the mutated regions, as illustrated in the pictogram in panel A. The arrows indicate the primer pairs used for PCR amplification. For the left side of the genome, PCR amplification results in a PCR product of 706 bp in the case of the wt genome but in no PCR product (due to the lack of the primer binding sites) in the case of the mutant genome. For the right side of the genome, PCR amplification results in a PCR product of 623 bp in the case of the wt genome and in a PCR product of 422 bp (due to the 201-bp deletion) in the case of the mutant genome. (Bottom) Virion DNAs were isolated from viruses reconstituted after cotransfection with either one or both of the fragments indicated in panel A, and the presence or absence of either the wt or mutated genomic fragment was investigated by PCR. Lanes 1, negative control (water); lanes 2, parental BAC; lanes 3, mutant E; lanes 4, mutant E plus cotransfection with the fragment spanning the deletion at the right side; lanes 5, mutant E plus cotransfection with the fragment spanning the deletion at the left side; lanes 6, mutant E plus cotransfection with both fragments. As expected, the wt pattern for the left side was restored after cotransfection with the left-side fragment or both fragments but not with the right-side fragment, and vice versa, i.e., the wt pattern for the right side was restored after cotransfection with the right-side fragment or both fragments but not with the left-side fragment.