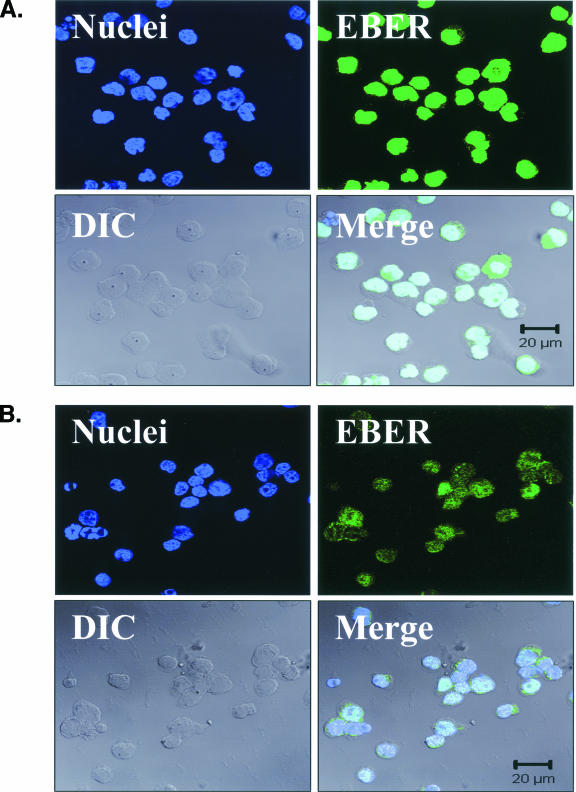
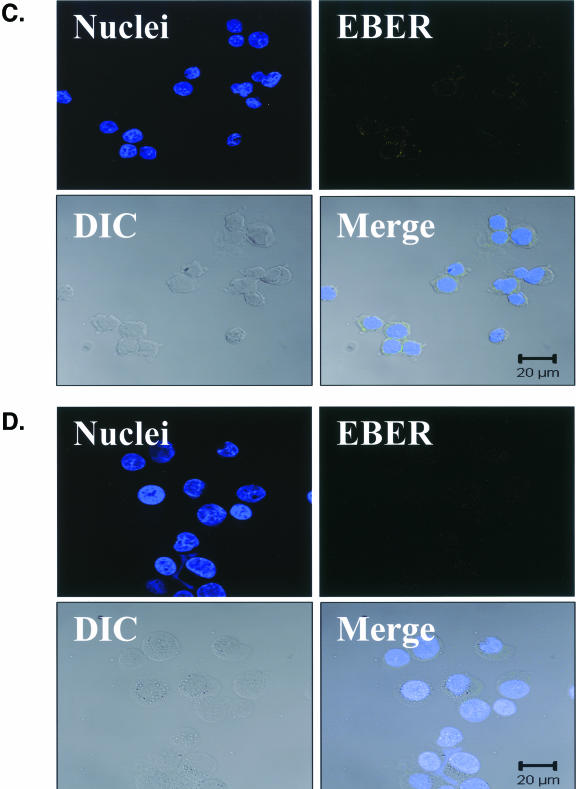
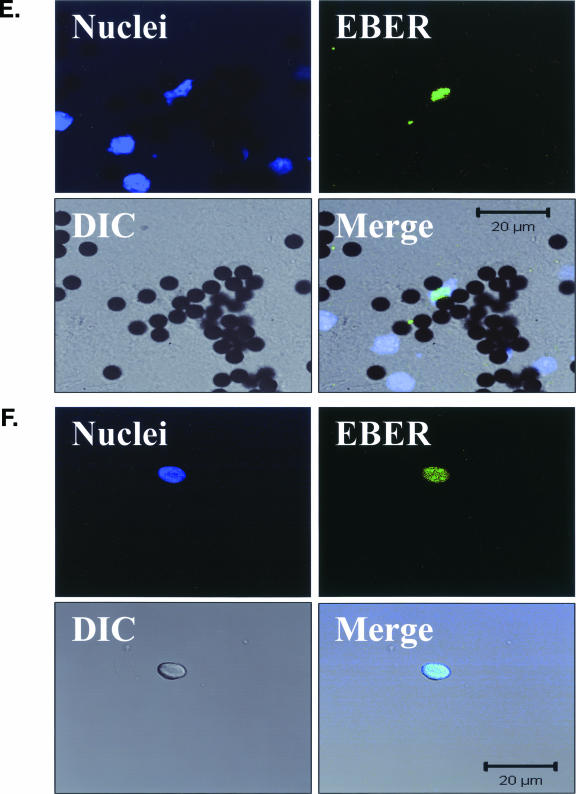
FIG. 4.
EBV EBER-FISH of pre-LC isolated from blood. Control cells and purified CD1a+ pre-LC isolated from the blood of healthy subjects were examined by in situ hybridization for latency-associated EBER transcription. Cells were imaged by fluorescent laser scanning confocal microscopy. DIC, Nomarski differential interference contrast. (A) EBV-positive Raji Burkitt's lymphoma cells express high levels of EBER (up to 105 or 106 transcripts per cell). Nuclear saturation of fluorescence was consistently detected. (B) EBV-positive Namalwa Burkitt's lymphoma cells express much lower levels of EBER (at least 100-fold lower than Raji cells). Variable levels of nuclear EBER expression were easily detected in most Namalwa cells. (C) EBV-negative BJAB Burkitt's lymphoma cells did not show EBER hybridization. (D) EBV-negative RHEK-1 epithelial cells did not show EBER hybridization. (E) Nuclear EBER expression was detected in a newly isolated CD1a+ pre-LC. The numerous black circles represent antibody-conjugated magnetic microbeads that are still attached to most of the CD1a+ cells, including the EBER-positive cell. (F) Nuclear EBER expression was detected in a CD1a+ pre-LC that was cultured in vitro for 3 days before EBER in situ hybridization.