FIG. 6.
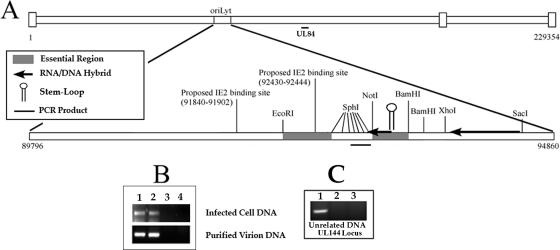
UL84 binds to the HCMV oriLyt within infected cells and purified virions. (A) Schematic of the HCMV origin of DNA replication showing the location within the HCMV genome as well as other distinguishing features including the relative locations of the regions essential for DNA synthesis, the RNA/DNA hybrid region, the SL-RNA stem-loop structure, the region amplified by PCR in the ChIP assay, and the proposed IE2 binding sites. (B) ChIP assay of AD169-infected cells and AD169 purified virion with the UL84-specific MAb (described in Materials and Methods). (Top panel) Lanes: 1, input control sample from infected-cell lysate amplified with oriLyt F and R primers; 2, ChIP sample from infected cell lysate amplified with oriLyt F and R primers; 3, no-antibody control ChIP sample from infected-cell lysate amplified with oriLyt F and R primers. (Bottom panel) Lanes: 1, input control sample from purified virion lysate amplified with oriLyt F and R primers; 2, ChIP sample from purified virion lysate amplified with oriLyt F and R primers; 3, ChIP sample from infected-cell lysate using the isotype control antibody amplified with oriLyt F and R primers; 4, no-antibody control ChIP sample from purified virion lysate amplified with oriLyt F and R primers. (C) ChIP assay of AD169-infected cells with the UL84-specific MAb amplified by primers corresponding to the UL144 locus. Lanes: 1, input control sample from infected-cell lysate amplified with UL144 primers; 2, ChIP sample from infected-cell lysate amplified with UL144 primers; 3, no-antibody control ChIP sample from infected-cell lysate amplified with UL144 primers.