FIG. 6.
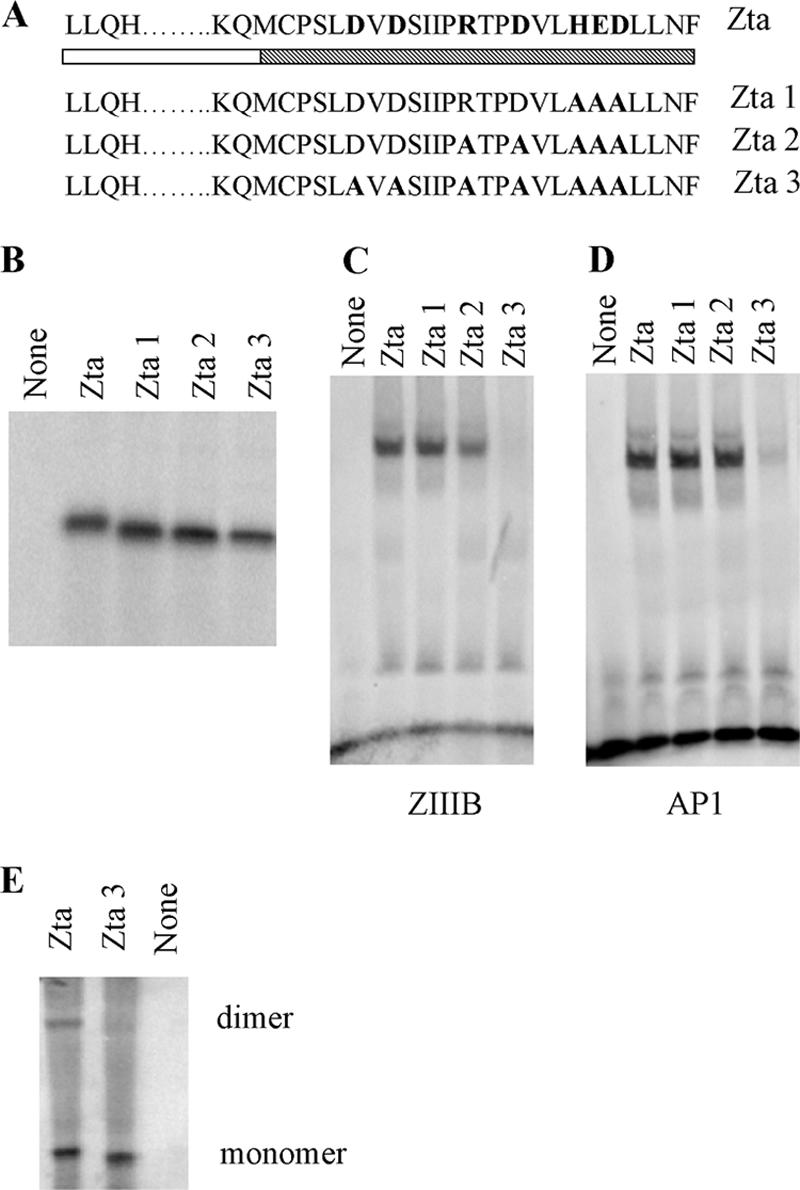
Importance of residues 226 and 228 for DNA-binding function of Zta. (A) Schematic representation of mutations of Zta1, Zta2, and Zta3, with the shading as described in Fig. 2. (B) Amounts of translation product generated for Zta and Zta truncated mutants used in the dimerization assay were assessed by SDS-PAGE and quantitated by phosphorimaging. (C and D) Equivalent amounts of protein were analyzed for their ability to bind DNA by EMSA analysis. Following separation of free and bound ZREs by electrophoresis, the locations of the complexes were detected using phosphorimaging, with subsequent quantitation. Duplicate experiments were undertaken, and representative images are shown for ZIIIB (C) and AP1 (D). (E) Equivalent amounts of protein were assessed for their abilities to form dimers as described in the legend to Fig. 2. Proteins of both monomer and dimer sizes are shown.
