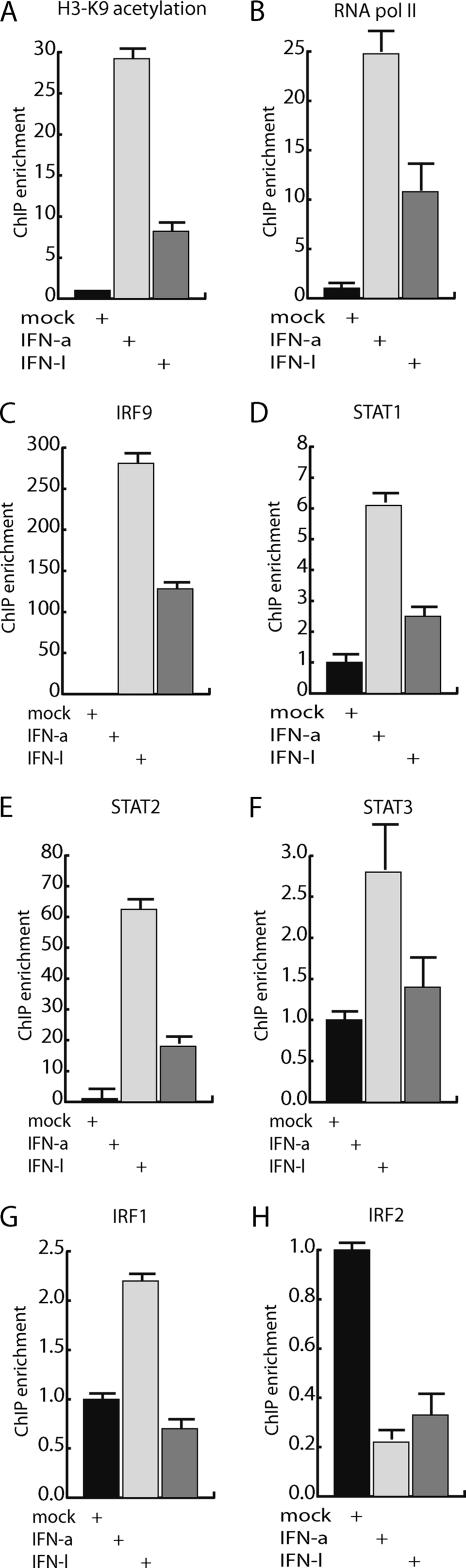
FIG. 2.
Transcription factor binding analysis of the ISG56 promoter after IFN-λ and IFN-α stimulation. The occupancy of transcription factors and histone modifications on the promoter region of ISG56 was determined by ChIP analysis. HepG2 cells were stimulated with either 0.05 μg/ml IFN-λ or 0.01 μg/ml IFN-α and used for the ChIP assay. The ChIP analysis was done with both specific and preimmunized antibodies to determine the unspecific level of precipitation of DNA. Real-time PCR analysis of the ChIP material was done with primers corresponding to the ISG56 5′-transcribed region and the GAPDH 5′-transcribed region (A and B, respectively) or with primers corresponding to the ISG56 promoter and the GAPDH promoter (C to H). All ChIP data were normalized to the GAPDH values and used as baseline values to determine experimental variation. All experiments were performed in triplicate. For cells not stimulated with IFN, the values obtained from the ChIP experiment were normalized to 1, and promoter fragment retention as a response to IFN was visualized. The ChIP analysis was performed with antibodies against (A) histone H3 lysine 9 (K9) acetylation, (B) RNA polymerase II, (C) IRF9, (D) STAT1, (E) STAT2, (F) STAT3, (G) IRF1, and (H) IRF2.