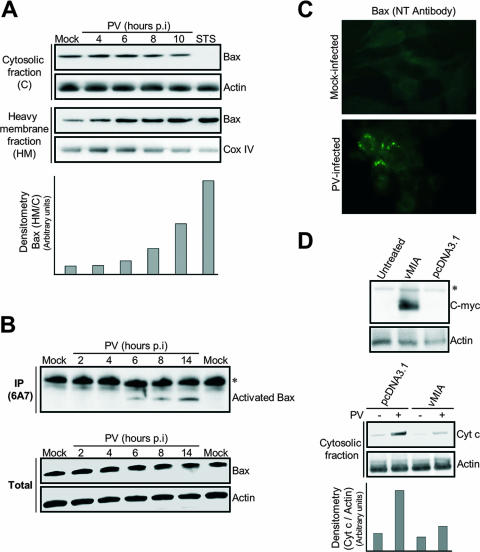
FIG. 3.
PV-mediated cytochrome c release in neuronal cells is Bax dependent. (A) Translocation of the proapoptotic protein Bax to mitochondria in PV-infected IMR5 cells. At the indicated time p.i., equal amounts of cytosolic and mitochondrial proteins were assayed for Bax by Western blotting. Mock-infected and STS-treated (8 h posttreatment) IMR5 cells were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. Cox IV and actin were used as protein loading controls for heavy membrane and cytosolic fractions, respectively. Protein levels of heavy membrane and cytosolic fractions were determined by densitometry and plotted as ratios relative to the levels of Cox IV and actin, respectively. (B) Time course of PV-induced Bax conformational change in IMR5 cells. (Top) Mock-infected and PV-infected IMR5 cells were lysed in immunoprecipitation buffer. Conformationally active Bax protein was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Bax 6A7 antibody and the precipitates were immunoblotted with anti-Bax antibody. The asterisk indicates immunoglobulin light chains. (Bottom) Whole-cell lysates that were not incubated with antibody were similarly tested for Bax by immunoblotting to check for equal amounts of Bax protein in samples prior to immunoprecipitation. Actin was used as protein loading controls. (C) PV-induced Bax activation. Mock-infected and PV-infected (6 h p.i.) IMR5 cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence with an antibody specific for the N terminus of Bax (NT antibody) to detect Bax conformational change. (D) Inhibition of cytochrome c release after vMIA expression in PV-infected IMR5 cells. (Top) Cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Myc-tagged vMIA, were transfected with empty vector (pcDNA3.1), or were left untreated. vMIA protein was detected in whole-cell lysates by Western blotting analysis with anti-Myc antibody. Actin was used as a protein loading control. The asterisk indicates a probable nonspecific protein band. (Bottom) Cytochrome c (Cyt c) release 24 h after transfection was analyzed in cytosolic fractions of mock-infected and PV-infected cells (8 h p.i.) by immunoblotting. Protein levels were determined by densitometry and plotted as ratios relative to the levels of actin.