Figure 3.
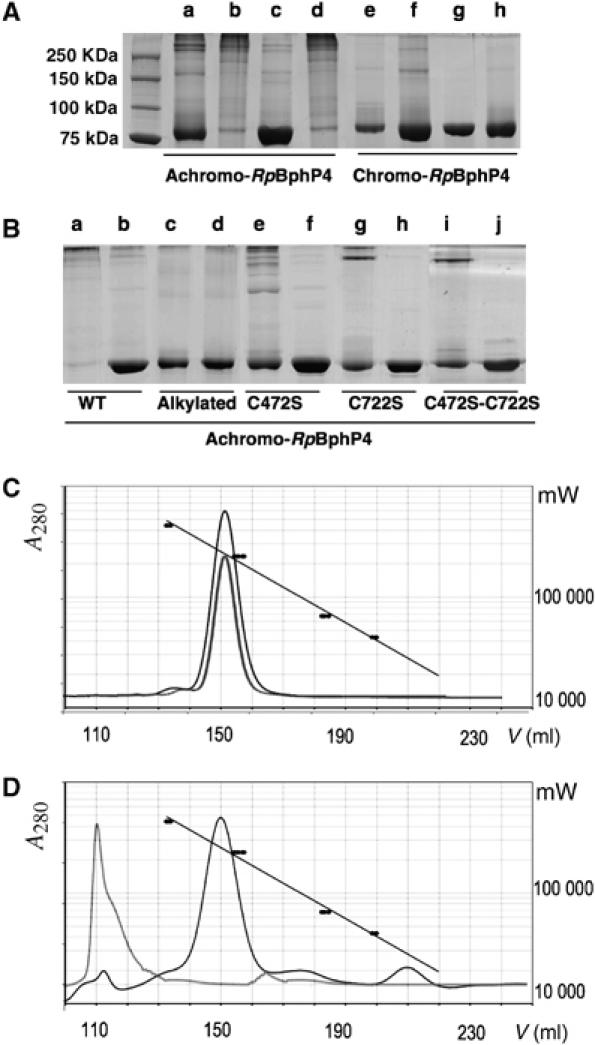
Redox dependence of achromo- and chromo-RpBphP4 proteins. SDS–PAGE analysis and gel filtration of RpBphP4 from CEA001 (achromo) or from HaA2 (chromo) after various treatments. (A) Lanes a and e show, respectively, untreated achromo- and chromo-RpBphP4 obtained after nickel affinity chromatography; lanes b and f show the effect of ultrafiltration (Amicon 30 K NMWL); lanes c and g show the effect of 1 mM DTT; and lanes d and h show the effect of 10 mM ferricyanide after reduction by 1 mM DTT. (B) Disulfide bond formation in achromo-RpBphP4 (WT), alkylated achromo-RpBphP4, RpBphP4-C472S, RpBphP4-C722S and RpBphP4-C472S-C722S, after oxidation with 1 mM ferricyanide (lanes a, c, e, g and i) or reduction with 1 mM DTT (lanes b, d, f, h and j). (C, D) Elution profiles of gel filtration of chromo-RpBphP4 (C) or achromo-RpBphP4 (D) in 50 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.0 in the absence (gray curves), or in the presence (black curves) of 10 mM DTT. A standard curve is superimposed using the known molecular masses of four protein standards (black circles).
