Figure 9.
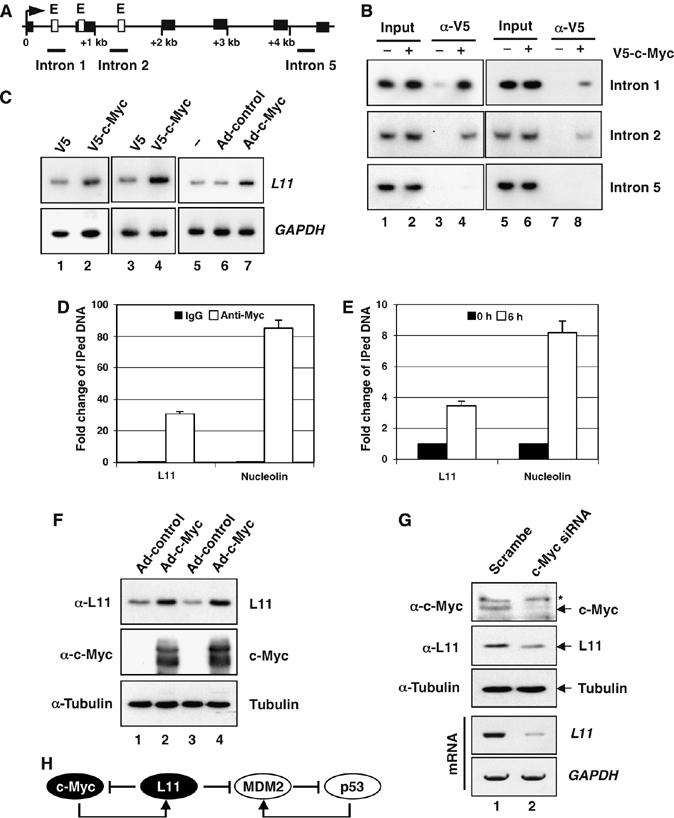
L11 is a target gene of c-Myc. (A) Diagram of the l11 gene exon–intron regions. Bars indicate the three regions amplified by ChIP-PCR assays. Empty boxes indicate E boxes. Filled boxes indicate exons. Arrow indicates the transcription start. (B) c-Myc specifically binds to the E box-containing introns 1 and 2, but not intron 5, regions of the l11 gene in H1299 (lanes 1 to 4) and U2OS (lanes 5 to 8) cells determined by ChIP-PCR assays. (C) c-Myc-induced l11 mRNA expression in cells. H1299 (lanes 1 to 2), U2OS (lanes 3 to 4), and WI38 cells (lanes 5 to 7) were transfected or infected with c-Myc-expressing plasmid or adenovirus and the expression of l11 was determined within 48 h by a semiquantitative RT–PCR assay. (D, E) Comparison of c-Myc binding to the L11 and the nucleolin gene promoters. (D) U2OS cells were subjected to ChIP assays using anti-c-Myc (N262) antibodies or control rabbit IgG followed by real-time PCR assays to detect the L11 and the nucleolin promoter DNAs. (E) U2OS cells were serum starved for 48 h, followed by stimulation with 20% FCS for 6 h as in Figure 6A. The serum-starved and re-stimulated cells were subjected to ChIP assays using anti-c-Myc (N262) antibodies, followed by real-time PCR to detect the L11 and the nucleolin promoter DNAs. (F) c-Myc induces L11 protein expression in cells. U2OS (lanes 1 and 2) and H1299 (lanes 3 and 4) cells were infected with c-Myc expressing adenovirus or control virus. Immunoblot (IB) was performed using antibodies as indicated. (G) Knockdown of endogenous c-Myc reduces L11 mRNA and protein levels. U2OS cells were transfected with c-Myc or scrambled siRNA. IB was performed using antibody as indicated and l11 mRNA was examined by a semiquantitative RT–PCR assay. *Indicates nonspecific band recognized by anti-c-Myc (N262). (H) A schematic for the L11-c-Myc feedback regulation versus the L11-MDM2-p53 regulatory loop.
