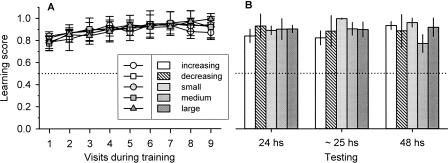
Figure 1.
Learning (A) and retention (B) scores (mean ± SEM), measured as the ratio between the number of inspections of the rewarded color and the total number of inspections of both colors, for the increasing (white circles and bars), decreasing (white squares and dashed bars), small (light gray circles and bars), medium (gray squares and bars), and large (dark gray triangles and bars) series. (Dotted lines) The score that would be expected via random choices: one-sample t-test, for learning score: increasing, t(6) = 8.3, P = 0.0002, N = 8; decreasing, t(7) = 4.6, P = 0.002, N = 9; small; t(8) = 8.4, P < 0.001, N = 9; medium; t(8) = 3.8, P = 0.005, N = 9; large; t(7) = 5.0, P = 0.001, N = 8; for retention score: increasing, 24 h, t(7) = 5.6, P = 0.0008, N = 8, ∼25 h, t(7) = 5.0, P = 0.0015, N = 8, 48 h, t(6) = 11.92, P < 0.0001, N = 7; decreasing, 24 h, t(8) = 11.5, P < 0.0001, N = 9, ∼25 h, t(6) = 5.4, P = 0.002, N∼25h = 7, 48 h, t(4) = 5.2, P = 0.007, N = 5; small, 24 h, t(8) = 9.9, P < 0.0001, N = 9, ∼25 h, t(8) = 93.5, P < 0.0001, N = 9, 48 h, t(6) = 11.3, P < 0.0001, N = 7; medium, 24 h, t(8) = 12.4, P < 0.0001, N = 9, ∼25 h, t(7) = 6.9, P = 0.0002, N = 8, 48 h, t(4) = 3.3, P = 0.02, N = 5; large, 24 h, t(7) = 12.0, P < 0.0001, N = 8, ∼25 h, t(7) = 5.8, P = 0.0006, N = 8, 48 h, t(3) = 5.0, P = 0.01, N = 4. One-way ANOVA for cumulative score learning (see Materials and Methods), F(4,37) = 0.7, P = 0.6. Kruskal–Wallis test for retention score, 24 h: H = 1.9, P = 0.7; ∼25 h: H = 7.8, P = 0.1; 48 h: H = 5.2, P = 0.3.