Figure 2.
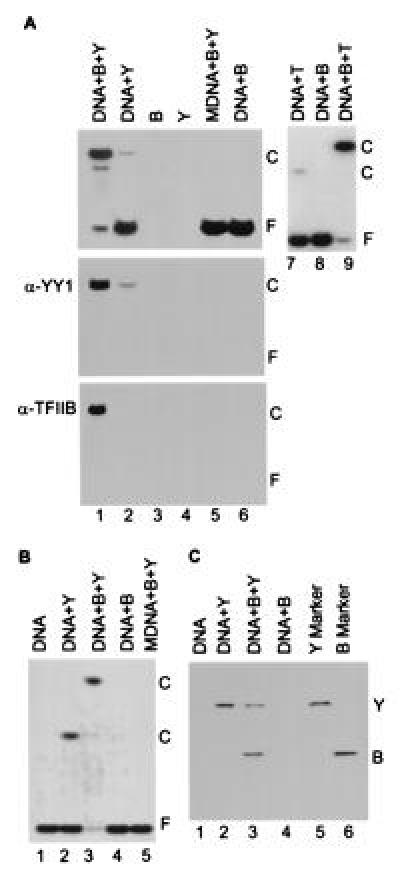
TFIIB forms a complex on DNA with YY1. (A) Band-shift assay of YY1–DNA interactions in a polyacrylamide gel. The components added to band-shift assays are indicated at the top of the autoradiograms. Lanes: B, TFIIB; Y, YY1; T, TBP; DNA, a 22-bp oligonucleotide with the YY1 binding site present at +1 in the AAV P5 promoter or a 20-bp oligonucleotide with the TATA motif present in the adenovirus major late promoter; and MDNA, a 22-bp derivative of the YY1-binding site to which YY1 cannot bind (14). (Top) Band-shift assay displays an autoradiogram where 32P-labeled probe DNA is detected. (Middle and Bottom) Protein blots using antibody to YY1 (α-YY1) or TFIIB (α-TFIIB). Reactions for band-shift assays in which proteins were transferred to membranes received 25-fold more of each protein than was used in standard band-shift assays. The positions of free DNA, F, and protein–DNA complexes, C, are indicated. (B) Band-shift assay in an agarose gel showing that TFIIB, YY1 and DNA form a complex. Components added to assays are as in A. The YY1–TFIIB–DNA complex was unstable during analysis in agarose, as evidenced by the substantial reduction in the amount of free DNA without a concomitant increase in the band corresponding to the complex (lane 3). (C) Analysis of proteins present in shifted complexes. Complexes present in the agarose gel displayed in B were excised, and their protein constituents were analyzed by electrophoresis in an SDS-containing polyacrylamide gel. Purified YY1 (Y) and TFIIB (B) were included as markers.
