Figure 2. DBC2 induction and CCND1 expression.
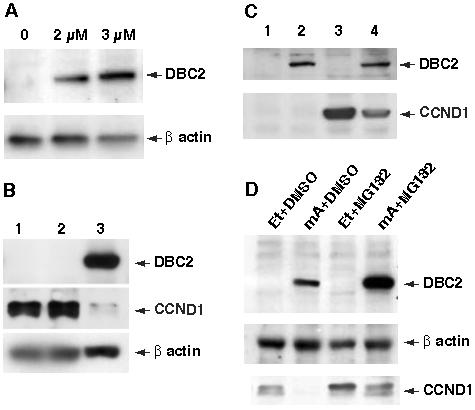
A. Induction of DBC2 by muristerone A (mA). 293A8 cells were cultured in a medium containing various concentrations of mA and examined for DBC2 expression by western blot analysis with anti-DBC2 antibody (N15). The concentration of mA is indicated at the top of each lane. B. DBC2 induction and endogenous CCND1. T-47D cells were cultured in DMEM (1), DMEM with ethanol (2) or DMEM with 5 μM muristerone A (3). The cells were harvested 6 hours after induction and analyzed by western blot analysis with anti-flag M2 antibody and anti-CCND1 antibody (M-20) (Santa Cruz Biotech, CA, USA). Drastic reduction of CCND1 protein in lane 3 was observed. C. 293A8 cells were transformed with either pCMV-CCND1 (lanes 3 and 4) or an empty vector (lanes 1 and 2). The transformants were cultured in DMEM with ethanol (lanes 1 and 3) or DMEM with 2 μM muristerone A (lanes 2 and 4) and then harvested 6 hours after induction. The cell lysates were analyzed by western blot analysis with anti-CCND1 antibody (M-20). Reduced CCND1 expression was noted when DBC2 was induced by muristerone A administration. D. DBC2 was induced in T-47D39 cells by culturing the cells in DMEM containing 5 μM muristerone A for 5 hours. The same amount of ethanol was added to the medium for the control. To inhibit 26S proteasome, the cells were incubated in a medium containing 50 μM MG132 for an hour until harvest. DMSO was added as a control. The cell lysates were analyzed by western blot analysis. Et and mA in the figure stand for ethanol and muristerone A, respectively.
