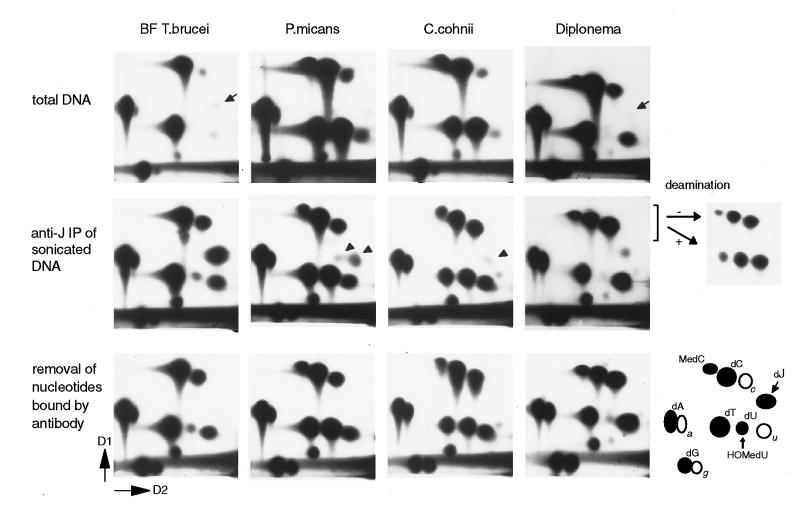
Figure 4.
Detection of J in Diplonema and J-like modifications in dinoflagellates. Analysis of bloodstream form T. brucei, P. micans, C. cohnii, and Diplonema by 32P-nucleotide postlabeling combined with 2D-TLC (D1 and D2 are indicated). The position of the labeled 5′-deoxynucleotidemonophosphates (dN) is explained in the right bottom corner. a, c, u, and g indicate contaminating ribonucleotides. dU and HOMedU nucleotides comigrate under these conditions. (Top) Labeling of total DNA. J is indicated with small arrows. (Middle) Analysis of samples after anti-J immunoprecipitation of sonicated DNA fragments. Arrowheads indicate nucleotides in dinoflagellates that migrate close to, but differently from, J. To test whether the nucleotide close to dC in Diplonema is 5-Me-dCMP, it was isolated together with dCMP and CMP, chemically deaminated (+), and rerun on 2D-TLC, mixed with nondeaminated input (−). Deamination of 5-Me-dCMP, dCMP, and CMP results in dTMP, dUMP, and UMP, respectively. (Bottom) Labeled nucleotides from the Middle were incubated with anti-J antibodies coupled to ProtA beads to specifically remove nucleotides recognized by the antibodies. The supernatant was analyzed by 2D-TLC.