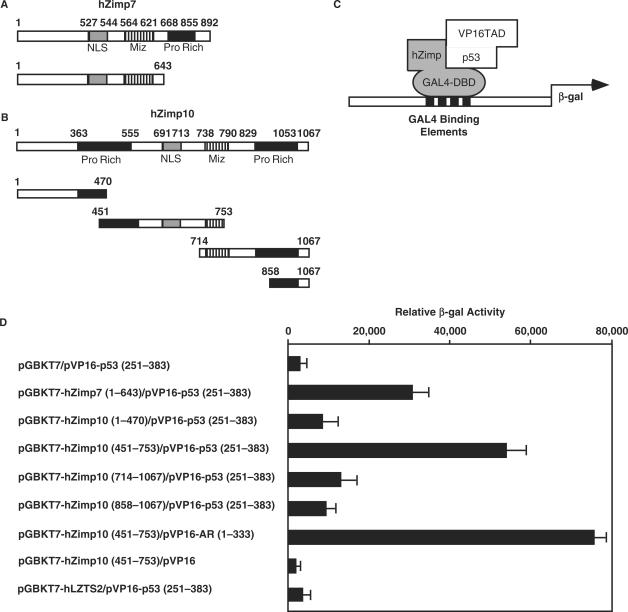
Figure 1.
Specific interaction between hZimp10 and p53. (A) and (B): The cDNA fragments containing different portions of human Zimp7, Zimp10 or human LZTS2 were fused to the GAL4-DBD in the pGBKT7 vector. Numbers correspond to amino acid residues. (C) A schematic representation of the yeast two-hybrid assay for mapping the interaction between p53, hZimp7 and hZimp10 proteins. (D) The pVP16-p53 containing the fusion protein of VP16-TAD and p53 (251–383) were co-transformed with pGBKT7 vector alone or different pGBKT7 fusion constructs. In addition, pVP16-AR (1–333) was included as a positive control, for the pGBKT7-hZimp10 (451–753). Transformed cells were plated on SD-Ade-Leu-Trp plates, and SD-Leu-Trp plates to monitor transformation efficiency. Three independent colonies were inoculated from each transformation experiment for subsequent liquid β-gal assays. The data for the liquid β-gal assays are shown as the mean ± S.D.