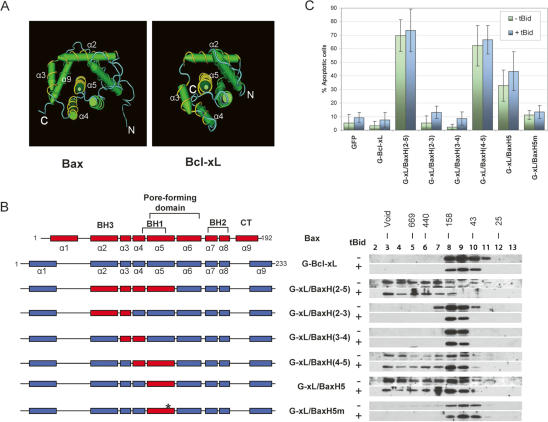
Figure 4.
Identification of structural determinant for homo-oligomerization by domain swapping between Bcl-xL and Bax. (A) Structural homology between Bax and Bcl-xL. The structural representation for Bax (1F16) (Suzuki et al. 2000) and Bcl-xL (1MAZ) (Muchmore et al. 1996) were taken from the NCBI Chemical Database. The helices highlighted with yellow are helices 2–5. Helix 5 in both Bax and Bcl-xL is perpendicular to the page, pointing outward. (B) The homo-oligomerization of the Bcl-xL/Bax chimeric proteins in the DKO cells. Schematic representations of wild-type Bax, Bcl-xL, and the chimeric proteins are shown on the left, with Bax helices shown in red and Bcl-xL helices in blue. Plasmids for the indicated Bcl-xL/Bax chimeras were transfected individually with or without the tBid expression plasmid into the DKO cells. Gel-filtration and Western blot analyses were carried out as described in Figure 1 and Materials and Methods. The asterisk indicates the alanine mutation in helix 5. (C) The apoptotic activities of Bcl-xL and the Bcl-xL/Bax chimeric proteins in DKO cells. The percentage of apoptotic cells was quantified as described in Figure 3B and Materials and Methods.