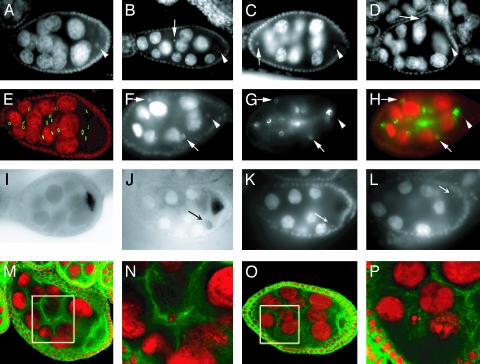
Fig. 6.
Egg chambers with defective oocyte determination in γTub23CPI fs(2)TW1RU34 mutant females. Egg chambers from WT (A, E, and I) or γTub23CPI fs(2)TW1RU34 (B-D, F-H, J-L, and M-P) females stained for DNA (gray in A-D, F, K, and L; red in E, H, and M-P), ring canals (gray in G, green in E and H) and microtubules (green in M-P). Posterior is to the right. (B-D) One of the two oocyte-like nuclei found within these egg chambers is always located posterior (arrowhead), as in the WT (A). The second oocyte-like nucleus (arrow) can be found anywhere within the egg chamber, posterior (D), anterior (C), or in the middle (B). It may have undergone a few rounds of endoreduplication in D.(F-H) One of the oocyte-like nuclei of this egg chamber is located posteriorly (arrowhead) within a cell with four ring canals (only two are visible). The oocyte has four ring canals in the WT (E). There are two more oocyte-like nuclei in the mutant egg chamber (arrows), located in cells with only one ring canal. H is a merge of F and G. (I and J) In situ hybridizations to osk mRNA. In the mutant (J) most signal is located within the posterior oocyte, similarly to what observed in a WT egg chamber (I), but there is also some accumulation of osk mRNA associated with the second oocyte-like cell (arrow in J). K and L are different focal planes of the egg chamber shown in J, stained with DAPI, to indicate the position of the oocyte nucleus (arrow in L) and the second oocyte-like nucleus (arrow in K). (M-P) Two examples of microtubule organization in 14 + 2 egg chambers at midoogenesis. N and P are higher-magnification images of the areas within the white boxes in M and O, respectively. In the egg chamber in M microtubules seem to accumulate around the second oocyte-like nucleus (N). No clear accumulation of microtubules close to the second oocyte-like nucleus can instead be detected in O and P. All images were obtained with conventional fluorescence microscopy, except E and M-P, which are confocal images, and I and J, which were obtained with phase-contrast microscopy. Egg chamber size is ≈150 μm.