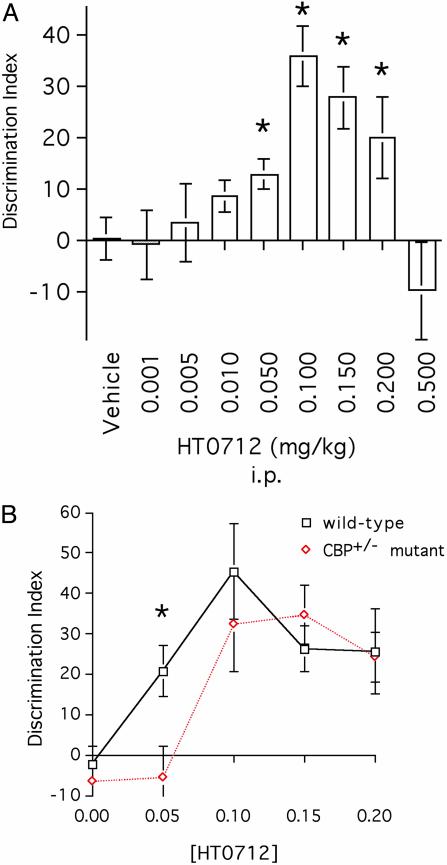
Fig. 3.
HT0712 dose sensitivity is decreased in mutant CBP+/− mice. (A) Dose-response curve for HT 0712 in wild-type mice. Mice received a single i.p. injection of drug or vehicle alone 20 min before training. Doses of 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, and 0.5 mg/kg were used. Animals experienced a 3.5-min training duration and were tested 24 h later (see Methods). Memory retention in drug-injected animals was significantly higher than that in vehicle-alone treated animals (n = 35) at doses of 0.05 mg/kg (n = 20; P < 0.05), 0.10 mg/kg (n = 22; P < 0.0001), 0.15 mg/kg (n = 18; P < 0.001), and 0.20 mg/kg (n = 17; P < 0.05). There were no significant effects at doses 0.001 mg/kg (P = 0.91; n = 6 for HT0712), 0.005 mg/kg (P = 0.72; n = 22 for HT0712), or 0.01 mg/kg (P = 0.34; n = 10 for HT0712). Because each session included vehicle-injected mice, the data for vehicle-injected mice were pooled. N values indicate a number of observations (repetitions) per treatment. (B) CBP+/− mutant mice are less sensitive than wild-type mice to the enhancing effects of HT 0712. CBP+/− mutants and wild-type mice received a single i.p. injection of vehicle or drug 20 min before training. They experienced a 3.5-min training duration and were tested 24-h later (see Methods). In wild-type mice, memory retention in drug-treated groups again was higher than in the vehicle-alone group (n = 26) at doses of 0.05 mg/kg (n = 12; P < 0.005), 0.10 mg/kg (n = 8; P < 0.0001), 0.15 mg/kg (n = 18; P < 0.005), and 0.2 mg/kg (n = 14; P < 0.005). In CBP+/− mutants, memory retention in drug-treated groups was higher than in the vehicle-alone group (n = 26) at doses of 0.10 mg/kg (n = 8; P < 0.0001), 0.15 mg/kg (n = 10; P < 0.0001), and 0.20 mg/kg (n = 14; P < 0.0001). In contrast to wild-type mice, a 0.05 mg/kg dose of HT0712 failed to enhance memory (n = 26; P = 0.79) in CBP+/− mutants. N values reflect number of observations (repetitions) per dose per genotype.