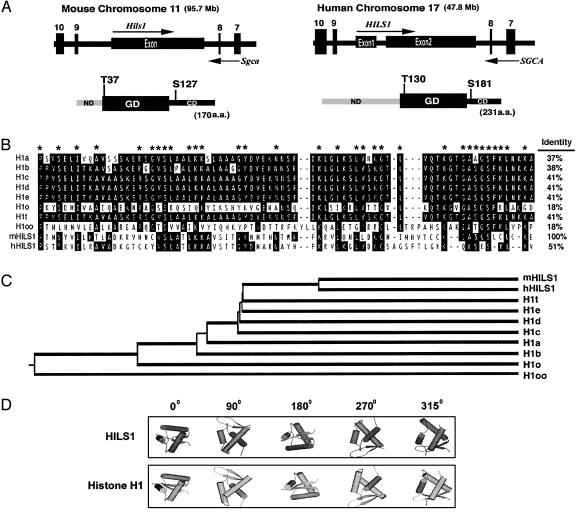
Fig. 2.
HILS1 genomic and protein structures. (A) Genomic organization and domain structures of the mouse and human HILS1 proteins. The mouse Hils1 is located in intron 8 of the mouse α-sarcoglycan gene (SGCA), and a similar genomic arrangement is conserved in humans. Arrows represent the transcriptional orientations of the genes. Each protein contains a globular domain (GD), which is flanked by an N-terminal domain (ND) and a C-terminal domain (CD). The conserved putative phosphorylation sites are marked. (B) Alignment analysis of the globular domains of histone H1 family members. Identical residues are highlighted, and residues conserved in at least 8 of 10 members are marked with asterisks. Amino acid identity between the globular domains of the mouse HILS1 and other family members is shown. (C) Phylogenetic tree of linker histone H1 family proteins. (D) Predicted 3D structure of mouse HILS1 versus histone H1a. Cylinders represent α-helical bundles, and arrows represent β-sheets. The angles of rotation are shown.