Figure 6.
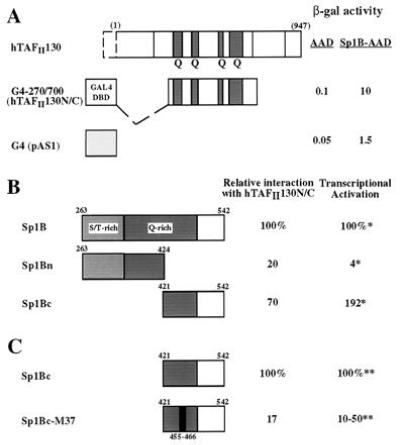
(A) Sp1-hTAFII130 interaction detected by yeast two-hybrid assay. hTAFII130N/C fused to the GAL4 DNA binding domain (residues 1–147, lightly shaded) is shown schematically. β-Galactosidase activity measured from lysates of yeast cotransformed with AAD fusions are indicated on the right. (B) hTAFII130 interacts preferentially with the C-terminal subdomain of Sp1 B that activates transcription in HeLa cells. Yeast plasmids containing the full-length Sp1 B domain (amino acids 263–542), or the subdivisions Bn (263-424), or Bc (421-542) fused to the acidic activation domain (8) were cotransformed with lexADBD-hTAFII130N/C fusion. The resulting β-galactosidase activity measured relative to the activity of the full-length Sp1 B, is indicated on the right. ∗, Previously reported relative values of transcriptional activation by equivalent fusion constructs expressed and assayed in HeLa cells (8). (C) A linker substitution mutation (indicated by the black bar) in the C-terminal subdomain of Sp1 B reduces both interaction with hTAFII130 and transcriptional activation in human cells. The yeast two-hybrid experiments were conducted as described for B. ∗∗, Transcriptional activation values measured in 293 cells by transient transfection were taken from (31) and S. Smale (personal communication).
