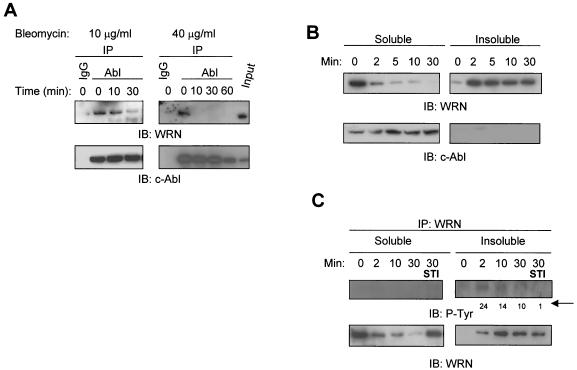
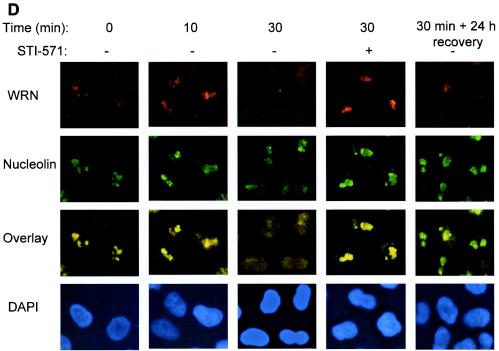
FIG.2.
Bleomycin-induced WRN tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation from c-Abl and c-Abl tyrosine kinase-dependent WRN relocalization. (A) HeLa cells were incubated with bleomycin (10 or 40 μg/ml for 0 to 60 min). Soluble cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-immunoglobulin G (IgG) or anti-Abl antibodies. The anti-Abl immunoprecipitates (IP) or input (10% of the amount for IP) were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-WRN antibodies and anti-Abl antibodies. (B and C) HeLa cells were incubated with bleomycin (40 μg/ml) with or without STI-571 pretreatment (1 μM, 24 h), and the soluble and insoluble lysates were IB with anti-WRN or anti-Abl antibodies. Alternatively, the anti-WRN IPs were analyzed by IB by using anti-phosphotyrosine (P-Tyr) antibodies followed by anti-WRN antibodies. The numbers indicated by an arrow are relative intensities of the bands. (D) HeLa cells were pretreated in the absence or presence of STI-571 (1 μM, 24 h) and then incubated with bleomycin (40 μg/ml) for 0 to 30 min. Some cells were replaced with normal medium 30 min after the bleomycin treatment and were stained 24 h thereafter. The cells were costained with rabbit anti-WRN (red) (Novus) and mouse anti-nucleolin (green) (MS-3; Santa Cruz) antibody and were visualized by a fluorescent microscope. The nuclei were stained with DAPI. +, present; −, absent.