Figure 2.
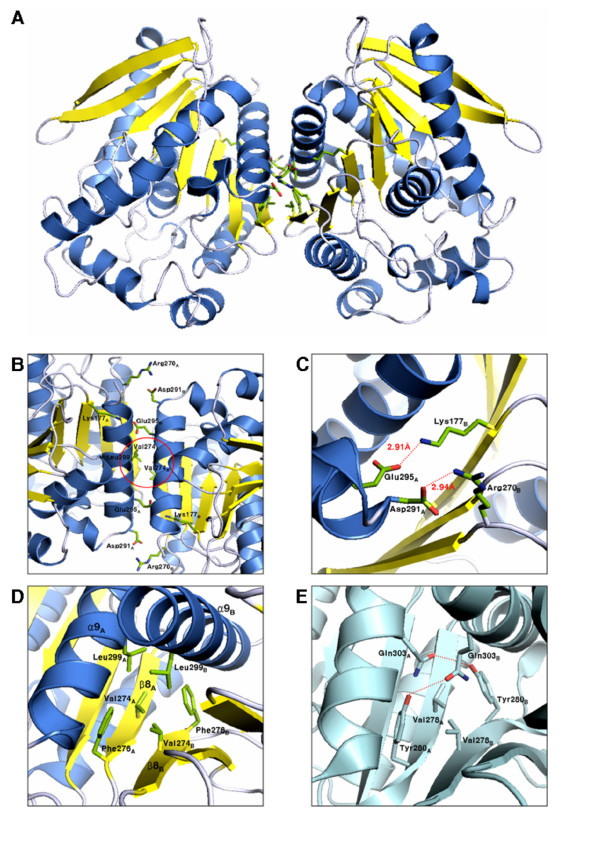
Structure of the EstE1 dimer. (A) The EstE1 dimer viewed along the crystallographic two-fold axis. Residues involved in hydrophobic interactions are shown in stick representation. Val274, Phe276, and Leu299 are involved in the hydrophobic interactions. Arg270-Asp291 and Lys177-Glu295 form salt bridges. (B) The centrosymmetric conformation of the interface between the two monomers, consisting of centric hydrophobic interactions (red circle) and salt bridges. (C) A detailed view of the salt bridges that support the dimeric conformation of EstE1. The side chain of Arg270B on the loop between the α8 helix and the β8 strand forms a salt bridge with Asp291A on the α9 helix. An additional salt bridge is formed between the side chains of Lys177B on the β6 strand and Glu295A on the α9 helix. (D) A detailed view of the hydrophobic interaction interface observed in the EstE1 dimer. The hydrophobic core residues (Leu299 on the α9 helix, and Phe276 and Val274 on the β8 strand) are indicated. (E) A detailed view of the interface observed in a current AFEST dimer model [19]. Dimeric interactions of AFEST are supported by hydrogen bonds between Tyr280 and Gln303, and by a weak hydrophobic interaction through Val278.
