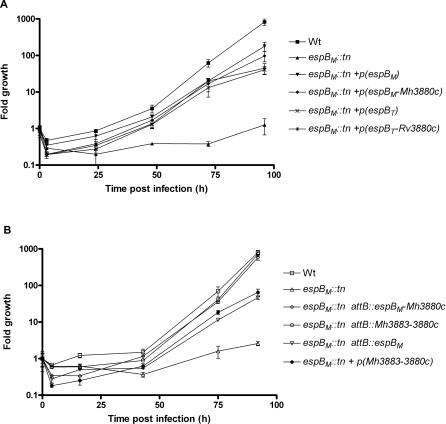
Figure 1. Either EspBT or EspBM Is Sufficient to Restore Growth to the espBM::tn Mutant in Mouse BMDMs.
BMDMs were infected at a multiplicity of infection of 1. Colony-forming units (cfu) were determined by lysing infected monolayers and plating lysates at indicated time points. Data were combined for three experiments, with growth indicated as fold increase compared to the initial level of infection for each strain.
(A) Wild type (Wt) and espBM::tn each contain the empty non-integrating plasmid pLYG206; p(espBM) and p(espBT) are plasmids for expression of EspBM and EspBT, respectively; and p(espBM-Mh3880c) and p(espBT-Rv3880c) encode the second gene of the operon as well as espB for each species.
(B) Wild type (Wt) and espBM::tn each were transformed with the empty integrating plasmid and the indicated genes were integrated into the attB of the espBM::tn mutant. espBM::tn + p(Mh3883c-Mh3880c) expresses the locus Mh3883-Mh3880c on a non-integrating plasmid. Strains differed significantly by one-way ANOVA in (A) after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h and in (B) after 16 h, 43 h, 75 h, and 92 h (p < 0.001 for each).