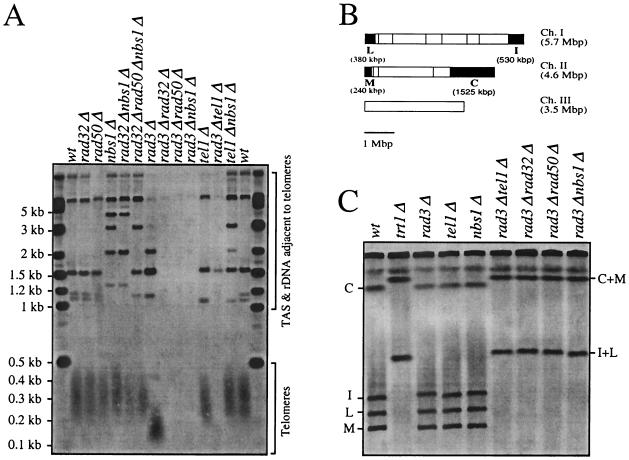
FIG. 3.
Nbs1 is involved in telomere-length maintenance. (A) Telomere length in wild-type (wt) (TMN2665), rad32Δ (TMN2799), rad50Δ (NR2840), nbs1Δ (TMN3224), rad32Δ nbs1Δ (CC3227), rad32Δ rad50Δ nbs1Δ (CC3229), rad3Δ (TMN2937), rad3Δ rad32Δ (TMN2994), rad3Δ rad50Δ (CC3233), rad3Δ nbs1Δ (CC3230), tel1Δ (TMN2967), rad3Δ tel1Δ (TMN3052) and tel1Δ nbs1Δ (CC3231) cells. A Southern blot of ApaI-digested S. pombe chromosomal DNA was hybridized to telomere-specific probes (44). The ApaI site is located in the telomere-associated sequence (TAS) 30 to 40 bp away from telomeric repeat sequences in both ends of chromosomes I and II and at least one end of chromosome III, giving rise to a broad ∼300-bp telomere hybridization signal in the wt strain (Telomeres). Hybridization signals (TAS & rDNA adjacent telomeres) come from cross-hybridization to TAS or hybridization to telomere(s) of chromosome III which contain rDNA repeats directly adjacent to the telomeric repeat sequence and therefore lack the TAS-associated ApaI site directly adjacent to the telomeric repeat sequence. (B) NotI restriction enzyme map of S. pombe chromosomes (vertical lines). The telomeric fragments C, I, L, and M are filled black. Chromosome III lacks a NotI site. (C) Chromosome structure in wt (TMN2665), trt1 (TMN2669), rad32 (TMN2799), tel1 (TMN2967), nbs1 (TMN3224), rad3 tel1 (TMN3052), rad3 rad32 (TMN2994), rad3 rad50 (CC3233), and rad3 nbs1 (CC3230) cells. A pulsed-field gel Southern blot of NotI-digested S. pombe chromosomal DNA was hybridized to C-, I-, L-, and M-specific probes (43). Four telomeric fragments (C, I, L, and M) and fusion products (C+M and I+L) are marked.