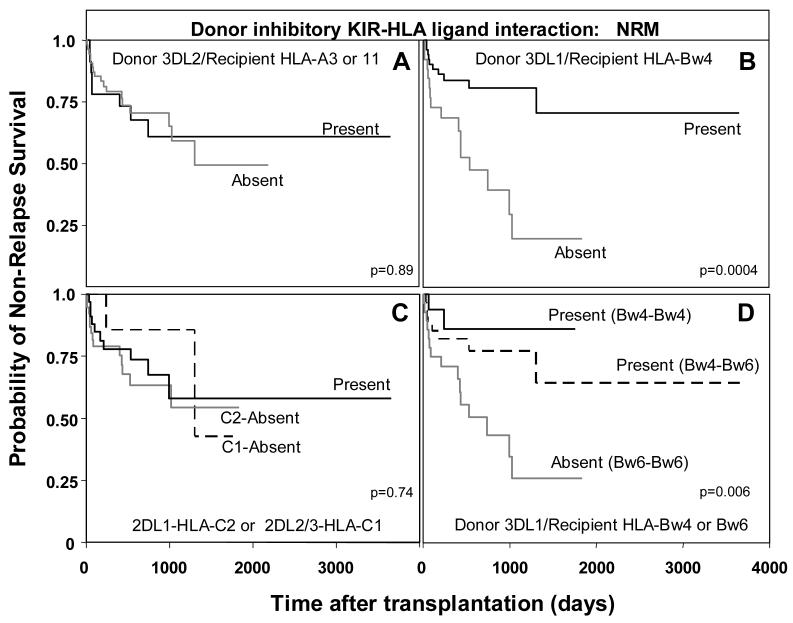
Figure 6.
Increased non-relapse mortality in AML/MDS patients (n=78) when the recipient lacks the Bw4 ligand for donor KIR3DL1. A. Kaplan-Meier analysis of non-relapse survival in AML/MDS patients (n=78) when: (A) the donor KIR3DL2-HLA-A3 or A11 ligand interaction is present (n=8/23) or absent (n=17/55, p=0.89); (B) when donor KIR3DL1-HLA-Bw4 ligand interaction is present (n=10/52) or absent (n=15/26, p=0.002; hazard ratio=3.6, 95% CI=1.6-8.4); and (C) when donor KIR2DL2/3-HLA-C1 or KIR2DL1-HLA-C2 interactions are present (n=10/33) or absent (C1 absent n=2/7, p=0.5; C2 absent n=13/38, p=0.76). D. Kaplan-Meier analysis of non-relapse survival in AML/MDS patients when donor KIR3DL1-HLA-B interactions are divided according to whether the donor is Bw4 homozygous or Bw4-Bw6 heterozygous. The equality of all three curves was tested (d.f.=2, p=0.006). Pairwise comparisons of all curves were then determined by Cox proportional hazard modeling, where the overall type I error rate was controlled by the initial test. Interactions between KIR3DL1 and HLA-Bw4 homozygous patients (n=2/16) were compared to interactions between KIR3DL1 and Bw4-Bw6 heterozygous patients (n=8/34, p=0.39), and to patients lacking the 3DL1-HLA-Bw4 ligand interaction (n=15/28, 0=0.03; hazard ratio=5.2, 95% CI=1.2-22.8).