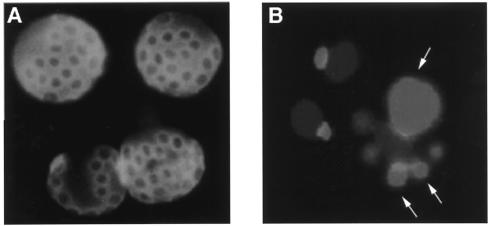
FIG. 1.
Yeast cell division and bud scar formation. (A) The budding of each daughter cell leaves a ring-shaped deposit, termed the bud scar, on the cell wall of the mother cell. These chitin-containing rings, formed at the neck of buds, can be stained with calcofluor, a fluorescent dye. The exact number of times an individual mother cell has undergone division can thus be determined by counting the number of bud scars present. (B) An aged yeast nucleus has an enlarged and fragmented nucleolus (arrows), unlike the nucleoli of two young cells in the upper left corner.