Figure 4.
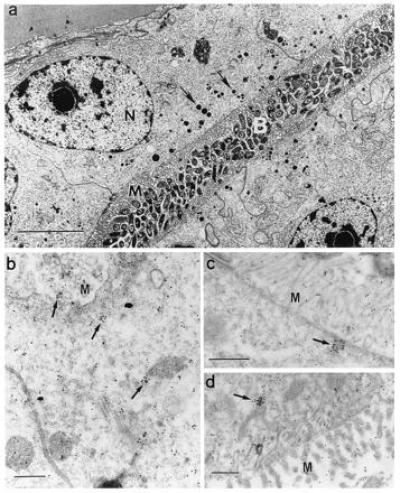
Cross-reactivity of squid tissues with polyclonal antibodies against native human MPO. (a) For reference and orientation, a low magnification micrograph of tissue fixed for conventional electron microscopy (7) illustrates the epithelial cells of the bacteria-containing region (nuclei, N), numerous microvilli (M) that extend into the bacteria-containing crypts (B), and vesicles (0.1–0.6 μm) along the apical surfaces of these cells (arrows). (Bar = 5 μm.) (b–d) Higher magnification micrographs of light organ tissues, fixed for immunocytochemistry, and reacted with antibodies against human MPO conjugated to gold spheres. (b and c) Apical surfaces of epithelial cells lining bacteria-containing crypts; numerous gold spheres occur singly and in clusters that average 1–2 μm (arrows). (d) Epithelia of the ciliated duct that connects the crypts with the exterior of the light organ, also with abundant gold spheres both alone and in clusters (arrow). M, epithelial microvilli. (Bars = 0.5 μm for b–d.)
