Figure 5.
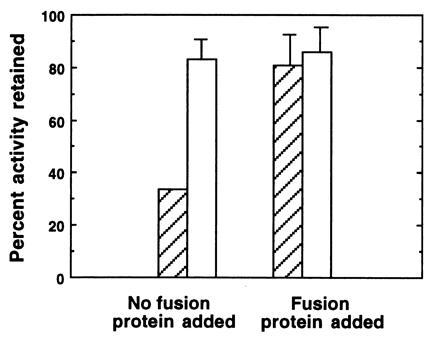
Immunoprecipitation of symbiotic organ extracts using anti-FPO. Tissues were dissected, homogenized and centrifuged as described in Fig. 2, except 0.05 M sodium phosphate with 0.1 M NaCl at pH 7.8 (PBS) was used as a buffer. In experimental trials (without fusion protein), 50 μl of the supernatant fluid were added to 10 μl of protein A Sepharose beads to which anti-FPO had been bound (hatched bars). To control for the potential effects of rabbit serum on enzyme activity, we also assayed samples in which 50 μl of supernatant fluid were added to 10 μl of Sepharose beads that had been preincubated with preimmune serum (open bars). In addition, in another set of controls, we determined whether the purified FPO could competitively inhibit binding of the putative peroxidase. In these experiments, 15 μl of a 2 mg/ml solution of purifed FPO in PBS were added to the supernatant fluid. To compensate for dilution effects, additional PBS was added to all samples for a final volume of 75 μl. In experimental and control samples, peroxidase activity was measured in all samples after a 24-h incubation period at 4°C. Bars are average percentages ± arcsine transformations (n = 5) of the initial peroxidase activity remaining in extracts after the 24-h incubation.
