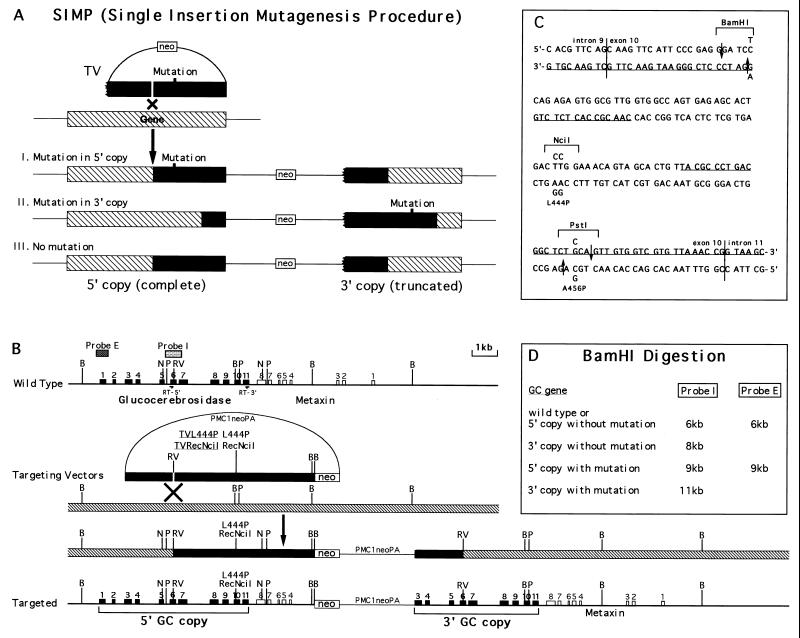
Figure 1.
Introduction of L444P and RecNciI human Gaucher disease mutations by the SIMP strategy. (A) A general scheme of the SIMP strategy. The ragged end of the gene in the targeting vector represents a truncation, filled bars represent the homology in the targeting vectors, hatched bars represent the endogenous allele. (B) The specific SIMP scheme for the introduction of the L444P and RecNciI mutations into the GC locus. The wild-type locus is shown on the top and the correctly targeted locus is shown on the bottom. The SIMP recombination step is shown in the middle. The filled boxes represent the exons of the GC gene, open boxes represent the exons of the nearby metaxin gene, stippled boxes represent probes used in the Southern analysis (probe I is a 0.7-kb KpnI fragment covering exon 6 and probe E is a 0.4-kb EcoRI fragment covering exon 1), filled bars represent the homology in the targeting vectors, hatched bars represent the endogenous allele. RT-5′, 5′ primer used in the reverse transcription (RT)-PCR primer (5′-CACGAATTCACATCACCCACTTGGCTCAAG-3′); RT-3′, 3′ primer used in the RT-PCR (5′-GTCGAATTCATGTCCATGCTAAGCCCAGGT-3′); B, BamHI; N, NciI; P, PstI; RV, EcoRV; Probe E, external probe; Probe I, internal probe. (C) The DNA sequence of the mouse GC exon 10 region. The vertical lines are exon/intron borders. The underlined sequences are oligonucleotides used in the RecA-assisted restriction endonuclease cleavage experiment. The mutations are indicated above and below the wild-type sequences. The mutated sequences between the two downward arrows were used as top strand of the mutation inserts. The mutated sequences between the two upward arrows were used as bottom strand of the mutation inserts. Both targeting vectors contained the change that eliminated the BamHI site and the L444P mutation. In addition, the RecNciI vector contain the L456P change. (D) The expected sizes of BamHI restriction fragments of wild-type and targeted GC genes detected by the I (internal) and E (external) probes.