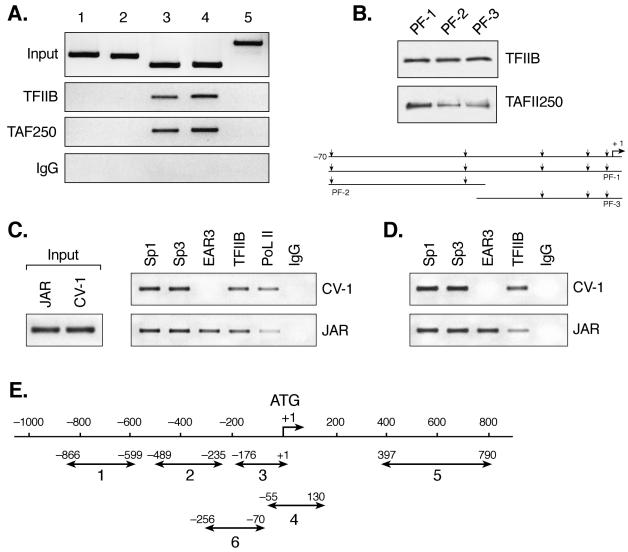
FIG. 7.
Recruitment of basal and trans-transcription factors to the hLHR gene promoter in JAR and CV-1 cells. (A) Recruitment of basal transcription factors, TFIIB and TAFII 250, to the hLHR gene promoter in ChIP assays. Soluble chromatin from JAR cells was precipitated with antibodies against TFIIB, TAFII 250, or preimmune rabbit or mouse immunoglobulin (row IgG). The DNA regions analyzed in PCR are schematically represented in panel E as follows: lanes 1 and 2 refer to 5′ flanking sequences to the promoter; lane 3 covers the full promoter region (positions −176 to +1); lane 4 encompasses the core promoter region only without upstream Sp1 and DR regulatory elements, and a short stretch of coding sequence downstream of ATG (+1); and lane 5 covers solely a part of coding region of the hLHR gene. The results of amplification of soluble chromatin before precipitation were shown as control (Input), and only the negative control with mouse IgG was shown as representative. (B) DAPAs of association of TFIIB or TAFII 250 to the hLHR gene core promoter region. The 5′ biotin-labeled probes utilized encompass DNA sequences of positions −70 to +1 (promoter fragment 1 [PF-1]), positions −70 to −30 (PF-2), and positions −34 to +1 (PF-3), respectively. The probes were incubated with JAR nuclear extracts, followed by immunodetection for bound TFIIB and TAFII 250. The region of the hLHR gene core promoter with arrows indicating the multiple transcription start sites is also shown. (C) ChIP analyses of the recruitment of Sp1, Sp3, EAR3, TFIIB, and RNA Pol II to the hLHR promoter region (region 3 in panel E) in CV-1 and JAR cells. Rabbit IgG was also included as negative control. (D) ChIP analyses of recruitment of Sp1, Sp3, EAR3, and TFIIB to region 6 (in panel E) in CV-1 and JAR cells. Region 6 covers the Sp1 sites and the DR motif of the hLHR gene promoter and some 5′ flanking sequences to the promoter but does not contain the core promoter region. (E) Schematic representation of DNA regions of hLHR gene analyzed in ChIP assays.